Toll-like receptor 4 mediates synergism between alcohol and HCV in hepatic oncogenesis involving stem cell marker Nanog
- PMID: 19171902
- PMCID: PMC2635765
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0807390106
Toll-like receptor 4 mediates synergism between alcohol and HCV in hepatic oncogenesis involving stem cell marker Nanog
Abstract
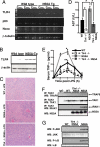
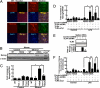
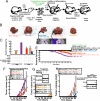
Alcohol synergistically enhances the progression of liver disease and the risk for liver cancer caused by hepatitis C virus (HCV). However, the molecular mechanism of this synergy remains unclear. Here, we provide the first evidence that Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is induced by hepatocyte-specific transgenic (Tg) expression of the HCV nonstructural protein NS5A, and this induction mediates synergistic liver damage and tumor formation by alcohol-induced endotoxemia. We also identify Nanog, the stem/progenitor cell marker, as a novel downstream gene up-regulated by TLR4 activation and the presence of CD133/Nanog-positive cells in liver tumors of alcohol-fed NS5A Tg mice. Transplantation of p53-deficient hepatic progenitor cells transduced with TLR4 results in liver tumor development in mice following repetitive LPS injection, but concomitant transduction of Nanog short-hairpin RNA abrogates this outcome. Taken together, our study demonstrates a TLR4-dependent mechanism of synergistic liver disease by HCV and alcohol and an obligatory role for Nanog, a TLR4 downstream gene, in HCV-induced liver oncogenesis enhanced by alcohol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
TLR4 Signaling via NANOG Cooperates With STAT3 to Activate Twist1 and Promote Formation of Tumor-Initiating Stem-Like Cells in Livers of Mice.Gastroenterology. 2016 Mar;150(3):707-19. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.11.002. Epub 2015 Nov 12. Gastroenterology. 2016. PMID: 26582088 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal regulation by TLR4 and TGF-β in tumor-initiating stem-like cells.J Clin Invest. 2013 Jul;123(7):2832-49. doi: 10.1172/JCI65859. Epub 2013 Jun 10. J Clin Invest. 2013. Retraction in: J Clin Invest. 2024 Oct 1;134(19):e186923. doi: 10.1172/JCI186923. PMID: 23921128 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Cancer stem cells generated by alcohol, diabetes, and hepatitis C virus.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Mar;27 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):19-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.07010.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 22320911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TLR4-dependent tumor-initiating stem cell-like cells (TICs) in alcohol-associated hepatocellular carcinogenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;815:131-44. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-09614-8_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 25427905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis C Virus nonstructural 5A protein inhibits lipopolysaccharide-mediated apoptosis of hepatocytes by decreasing expression of Toll-like receptor 4.J Infect Dis. 2011 Sep 1;204(5):793-801. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir381. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21844306
Cited by
-
Alcohol, nutrition and liver cancer: role of Toll-like receptor signaling.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Mar 21;16(11):1344-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i11.1344. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20238401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Starring role of toll-like receptor-4 activation in the gut-liver axis.World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2015 Nov 15;6(4):99-109. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v6.i4.99. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2015. PMID: 26600967 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring a common mechanism of alcohol-induced deregulation of RNA Pol III genes in liver and breast cells.Gene. 2017 Aug 30;626:309-318. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.05.048. Epub 2017 May 25. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28552569 Free PMC article.
-
HCV and tumor-initiating stem-like cells.Front Physiol. 2022 Sep 15;13:903302. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.903302. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36187761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dedifferentiation process driven by radiotherapy-induced HMGB1/TLR2/YAP/HIF-1α signaling enhances pancreatic cancer stemness.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Sep 26;10(10):724. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1956-8. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31558702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Okuda K. Hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2000;32:225–237. - PubMed
-
- Okuda MK, et al. Mitochondrial injury, oxidative stress, and antioxidant gene expression are induced by hepatitis C virus core protein. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:366–375. - PubMed
-
- Yao F, Terrault N. Hepatitis C and hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2001;2:473–483. - PubMed
-
- Heintges T, Wands JR. Hepatitis C virus: Epidemiology and transmission. Hepatology. 1997;26:521–526. - PubMed
-
- Brechot C, Nalpas B, Feitelson MA. Interactions between alcohol and hepatitis viruses in the liver. Clin Lab Med. 1996;16:273–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

