Anticancer alkaloid lamellarins inhibit protein kinases
- PMID: 19172192
- PMCID: PMC2630805
- DOI: 10.3390/md20080026
Anticancer alkaloid lamellarins inhibit protein kinases
Abstract
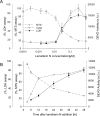
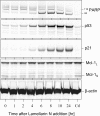
Lamellarins, a family of hexacyclic pyrrole alkaloids originally isolated from marine invertebrates, display promising anti-tumor activity. They induce apoptotic cell death through multi-target mechanisms, including inhibition of topoisomerase I, interaction with DNA and direct effects on mitochondria. We here report that lamellarins inhibit several protein kinases relevant to cancer such as cyclin-dependent kinases, dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation activated kinase 1A, casein kinase 1, glycogen synthase kinase-3 and PIM-1. A good correlation is observed between the effects of lamellarins on protein kinases and their action on cell death, suggesting that inhibition of specific kinases may contribute to the cytotoxicity of lamellarins. Structure/activity relationship suggests several paths for the optimization of lamellarins as kinase inhibitors.
Keywords: CK1; DYRK-1A; GSK-3; cyclin-dependent kinases; kinase inhibitor; lamellarin.
Figures
References
-
- Bourguet-Kondracki ML, Kornprobst JM. Marine pharmacology: potentialities in the treatment of infectious diseases, osteoporosis and Alzheimer's disease. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2005;97:105–131. - PubMed
-
- Simmons TL, Andrianasolo E, McPhail K, Flatt P, Gerwick WH. Marine natural products as anticancer drugs. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005;4:333–342. - PubMed
-
- Cironi P, Albericio F, Alvarez M. Lamellarins: isolation, activity and synthesis. Progr. Heterocycl. Chem. 2004;16:1–26.
-
- Bailly C. Lamellarins, from A to Z: a family of anticancer marine pyrrole alkaloids. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti-Cancer Agents. 2004;4:363–378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
