Metastatic tumour cells favour the generation of a tolerogenic milieu in tumour draining lymph node in patients with early cervical cancer
- PMID: 19172271
- PMCID: PMC11030623
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-008-0646-7
Metastatic tumour cells favour the generation of a tolerogenic milieu in tumour draining lymph node in patients with early cervical cancer
Abstract
Objective: We compared the immune system state in metastatic tumour draining lymph nodes (mTDLN) and metastasis free TDLN (mfTDLN) in 53 early stage cervical cancer patients to assess whether the presence of metastatic tumour cells worsen the balance between an efficacious anti-tumour and a tolerogenic microenvironment.
Methods: The immune system state was measured by immunophenotypic and functional assessment of suppressor and effector immune cell subsets.
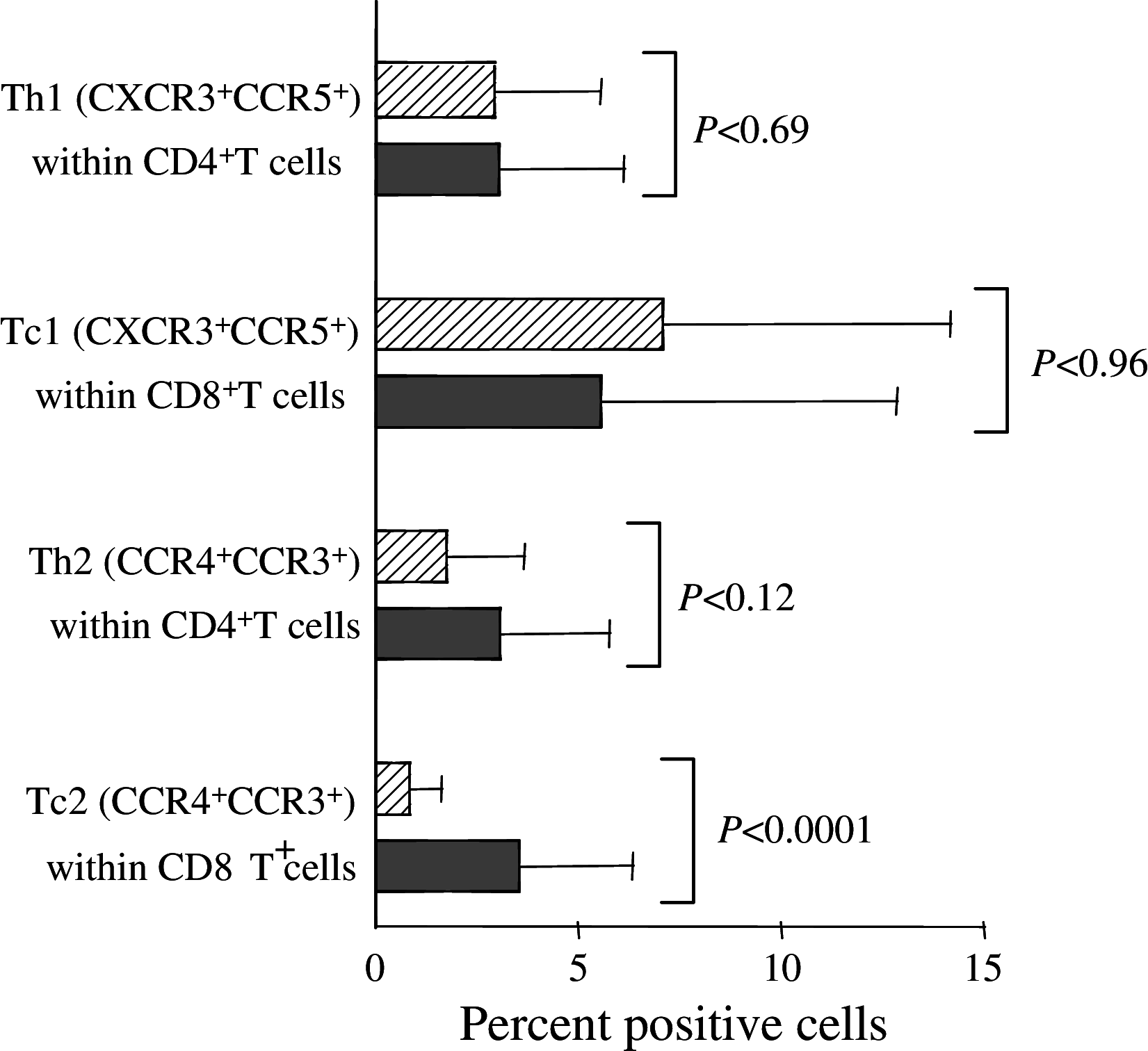
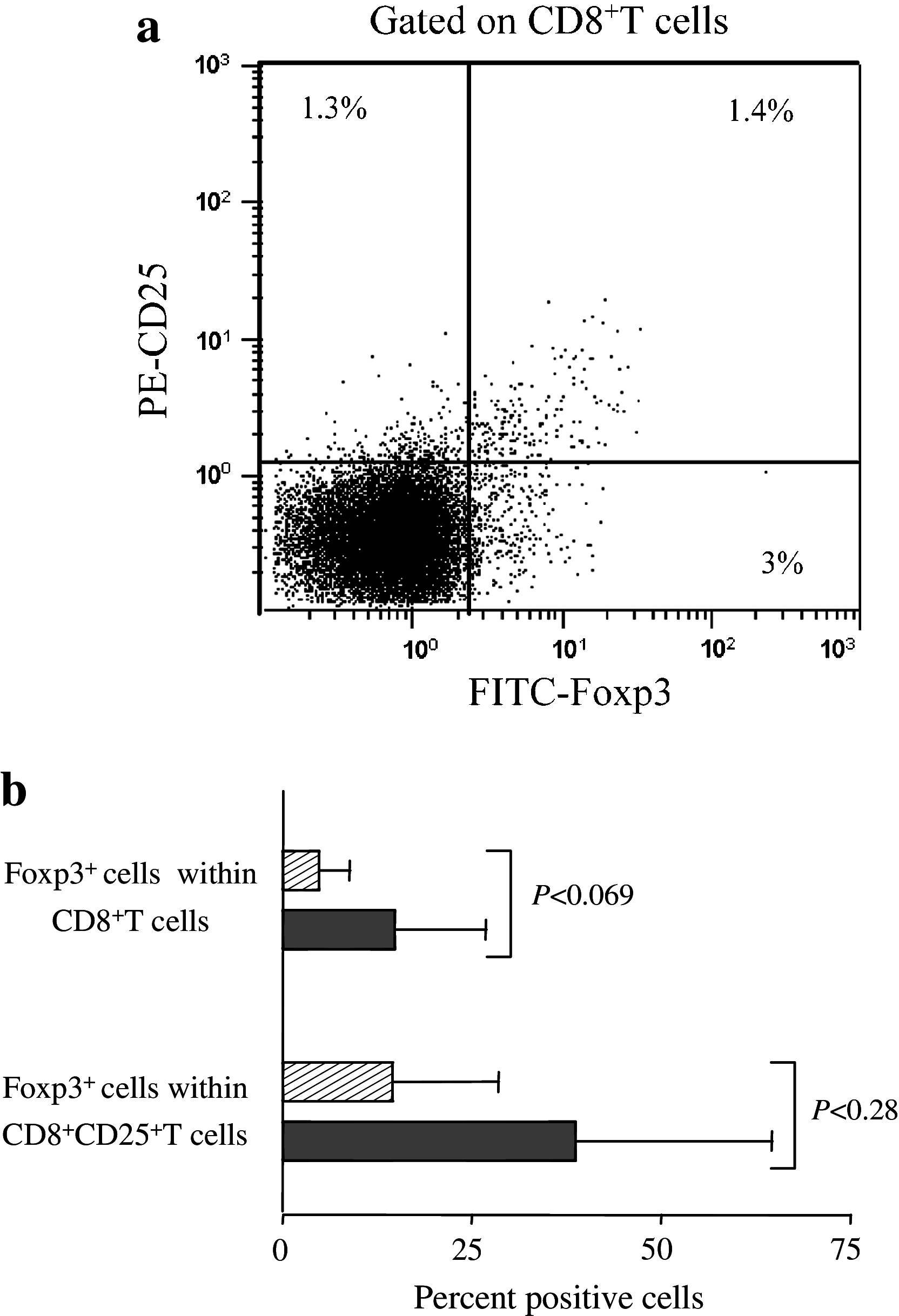
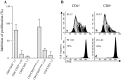
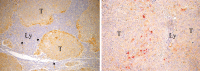
Results: Compared to mfTDLN, mTDLN were significantly enriched in CD4(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells (Treg), which, in addition, exhibited an activated phenotype (HLA-DR(+) and CD69(+)). Treg in mTDLN were also significantly enriched in neuropilin-1 (Nrp1) expressing cells, a subset particularly potent in dampening T cell responses. mTDLN tended to be enriched in a population of CD8(+)Foxp3(+)T cells (operationally defined as CD8(+)Treg) that showed a suppressor potency similar to Treg under the same experimental conditions. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC) and myeloid DC (mDC) generally show distinct roles in inducing T cell tolerance and activation, respectively. In line with the excess of suppressor T cells, the ratio pDC to mDC was significantly increased in mTDLN. Immunohistochemical testing showed that metastatic tumour cells produced the vascular endothelial growth factor, a natural ligand for Nrp1 expressed on the cell surface of Nrp1(+)Treg and pDC, and therefore a potential mediator by which tumour cells foster immune privilege in mTDLN. Consistent with the overall tolerogenic profile, mTDLN showed a significant Tc2 polarisation and tended to contain lower numbers of CD45RA(+)CD27(-) effector memory CD8(+)T cells.
Conclusions: The increased recruitment of suppressor type cells concomitant with the scarcity of cytotoxic type cells suggests that in mTDLN the presence of tumour cells could tip the balance against anti-tumour immune response facilitating the survival of metastatic tumour cells and possibly contributing to systemic tolerance.
Figures
References
-
- Baars PA, Ribeiro Do Couto LM, Leusen JH, Hooibrink B, Kuijpers TW, Lens SM, van Lier RA. Cytolytic mechanisms and expression of activation-regulating receptors on effector-type CD8+CD45RA+CD27− human T cells. J Immunol. 2001;165:1910–1917. - PubMed
-
- Barbera-Guillem E, Nyhus JK, Wolford CC, Friece CR, Sampsel JW. Vascular endothelial growth factor secretion by tumor-infiltrating macrophages essentially supports tumor angiogenesis, and IgG immune complexes potentiate the process. Cancer Res. 2002;62:7042–7049. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia A, Buzzonetti A, Monego G, Peri L, Ferrandina G, Fanfani F, Scambia G, Fattorossi A. Neuropilin-1 expression identifies a subset of regulatory T cells in human lymph nodes that is modulated by pre-operative chemoradiation therapy in cervical cancer. Immunology. 2008;123:129–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02737.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Battaglia A, Ferrandina G, Buzzonetti A, Malinconico P, Legge F, Salutari V, Scambia G, Fattorossi A. Lymphocyte populations in human lymph nodes. Alterations in CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cell phenotype and T-cell receptor Vβ repertoire. Immunology. 2003;110:304–312. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01742.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

