Functional characterization of N297A, a murine surrogate for low-Fc binding anti-human CD3 antibodies
- PMID: 19172487
- PMCID: PMC2646398
- DOI: 10.1080/08820130802608238
Functional characterization of N297A, a murine surrogate for low-Fc binding anti-human CD3 antibodies
Abstract
Several low- or non-FcR binding anti-human CD3 monoclonal antibodies have been under investigation for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. To model the mechanism of action of these anti-human CD3 mAbs in the murine system, an Fc-modified anti-mouse CD3 antibody (N297A) was generated. N297A exhibited similar biological effects as Fc-modified anti-human CD3 antibodies including rapid, reversible reduction in peripheral leukocyte numbers, differential modulation of activated versus resting T cells, and reduced levels of induced cytokine release compared to the non-Fc-modified parent antibody. In an in vivo model of colitis induced by adoptive transfer of IL-10-deficient cells, administration of N297A significantly reduced body weight loss. As N297A shared many functional characteristics of non-FcR binding anti-human CD3 mAbs both in vitro and in vivo, it provides a means to model the mechanisms of action of Fc-modified anti-human CD3 antibodies in mouse.
Figures
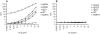

 ). (C+D) Spleen cells from BALB/c mice were treated with WT (□), N297A (▴), or NCNS-1 negative control (
). (C+D) Spleen cells from BALB/c mice were treated with WT (□), N297A (▴), or NCNS-1 negative control ( ) mAb for 24 hours with either no prior activation (C) or prior stimulation with Con A for 96 hours (D). Apoptotic cells were then stained using TACS Annexin V/PI kit. Cells that did not stain for Annexin V or PI were calculated and shown as % of viable cells. Triplicate samples for each condition were analyzed and average values are shown in the graphs.
) mAb for 24 hours with either no prior activation (C) or prior stimulation with Con A for 96 hours (D). Apoptotic cells were then stained using TACS Annexin V/PI kit. Cells that did not stain for Annexin V or PI were calculated and shown as % of viable cells. Triplicate samples for each condition were analyzed and average values are shown in the graphs.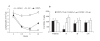
 ) mAb. Blood samples from 5 mice per group were collected in EDTA coated tubes at indicated time points for total lymphocyte counts. (B) Different dose levels of N297A (10 μg, black bars, or 1 μg, white bars) or NCNS-1 (dotted bars) were injected i.v. into naïve C57/B6 mice at day 0 (n=5). The mice were bled at the indicated time point, and CD4+ T cells were quantified by flow cytometry using TruCOUNT reagents; counts per μl are shown. An unpaired two-tailed t-test was used for statistical analysis. *p=0.0002 for N297A (10 μg) vs. NCNS-1; # p=0.019 for N297A (1 μg) vs. NCNS-1 at day 1. The differences at other time points were not statistically significant.
) mAb. Blood samples from 5 mice per group were collected in EDTA coated tubes at indicated time points for total lymphocyte counts. (B) Different dose levels of N297A (10 μg, black bars, or 1 μg, white bars) or NCNS-1 (dotted bars) were injected i.v. into naïve C57/B6 mice at day 0 (n=5). The mice were bled at the indicated time point, and CD4+ T cells were quantified by flow cytometry using TruCOUNT reagents; counts per μl are shown. An unpaired two-tailed t-test was used for statistical analysis. *p=0.0002 for N297A (10 μg) vs. NCNS-1; # p=0.019 for N297A (1 μg) vs. NCNS-1 at day 1. The differences at other time points were not statistically significant.
 ) and WT (□) mAb. Mice that did not receive any OVA-activated cells (No cells •) were used as control.
) and WT (□) mAb. Mice that did not receive any OVA-activated cells (No cells •) were used as control.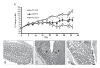
 ) 2 to 3 times a week for a total of six doses starting at day 20. No cell control group (❍) did not receive any T cells and thus continued to grow and gain body weight (n=6). Percent change in body weight (BW) was calculated by subtracting body weight on day of measurement from ody weight on day 0 and divided by the initial body weight. Statistical significance was assessed at each time point using an unpaired, two-tailed t-test to derive the p values between N297A and NCNS-1 groups (*p < 0.05). (B-D) Representative histological images of the IBD study. (B) Normal colon of control mice that did not receive T cells. Colons of IBD mice that were treated with 10 μg of NCNS-1 (C) or N297A (D). The colons were harvested at the end of study and stained with H/E for morphology. The slides were reviewed by a certified pathologist. Severe inflammation and crypts filled with neutrophils were observed (arrows) in the colons of most NCNS-1 treated mice.
) 2 to 3 times a week for a total of six doses starting at day 20. No cell control group (❍) did not receive any T cells and thus continued to grow and gain body weight (n=6). Percent change in body weight (BW) was calculated by subtracting body weight on day of measurement from ody weight on day 0 and divided by the initial body weight. Statistical significance was assessed at each time point using an unpaired, two-tailed t-test to derive the p values between N297A and NCNS-1 groups (*p < 0.05). (B-D) Representative histological images of the IBD study. (B) Normal colon of control mice that did not receive T cells. Colons of IBD mice that were treated with 10 μg of NCNS-1 (C) or N297A (D). The colons were harvested at the end of study and stained with H/E for morphology. The slides were reviewed by a certified pathologist. Severe inflammation and crypts filled with neutrophils were observed (arrows) in the colons of most NCNS-1 treated mice.References
-
- Alegre M.L., Tso J.Y., Sattar H.A., Smith J., Desalle F., Cole M., Bluestone J. A. An anti-murine CD3 monoclonal antibody with a low affinity for Fc gamma receptors suppresses transplantation responses while minimizing acute toxicity and immunogenicity. J. Immunol. 1995;155:1544–1555. - PubMed
-
- Alegre M.L., Vandenabeele P., Depierreux M., Florquin S., Deschodt-Lanckman M., Flamand V., Moser M., Leo O., Urbain J., Fiers W., et al. Cytokine release syndrome induced by the 145–2C11 anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody in mice prevention by high doses of methylprednisolone. J. Immunol. 1991;146:1184–1191. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter P.A., Appelbaum F.R., Corey L., Deeg H.J., Doney K., Gooley T., Krueger J., Martin P., Pavlovic S., Sanders J., et al. A humanized non-FcRbinding anti-CD3 antibody, visilizumab, for treatment of steroid-refractory acute graftversus-host disease. Blood. 2002;99:2712–2719. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter P.A., Lowder J., Johnston L., Frangoul H., Khoury H., Parker P., Jerome K.R., McCune J.S., Storer B., Martin P., et al. A phase II multicenter study of visilizumab, humanized anti-CD3 antibody, to treat steroidrefractory acute graft-versushost disease. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005;11:465–471. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
