The impact of maternal obesity on maternal and fetal health
- PMID: 19173021
- PMCID: PMC2621047
The impact of maternal obesity on maternal and fetal health
Abstract
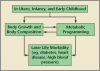
The increasing rate of maternal obesity provides a major challenge to obstetric practice. Maternal obesity can result in negative outcomes for both women and fetuses. The maternal risks during pregnancy include gestational diabetes and preeclampsia. The fetus is at risk for stillbirth and congenital anomalies. Obesity in pregnancy can also affect health later in life for both mother and child. For women, these risks include heart disease and hypertension. Children have a risk of future obesity and heart disease. Women and their offspring are at increased risk for diabetes. Obstetrician-gynecologists are well positioned to prevent and treat this epidemic.
Keywords: Birth outcomes; Diabetes; Fetal health; Maternal health; Obesity.
Figures
References
-
- Lynch CM, Sexton DJ, Hession M, Morrison JJ. Obesity and mode of delivery in primigravid and multigravid women. Am J Perinatol. 2008;25:163–167. - PubMed
-
- Rooney B, Schauberger C. Excess pregnancy weight gain and long-term obesity: one decade later. Obstet Gynecol. 2002;100:245–252. - PubMed
-
- de Boo HA, Harding JE. The developmental origins of adult disease (Barker) hypothesis. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2006;46:4–14. - PubMed
-
- Whitaker RC. Predicting preschooler obesity at birth: the role of maternal obesity in early pregnancy. Pediatrics. 2004;114:e29–e36. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources