Genomic location analysis by ChIP-Seq
- PMID: 19173299
- PMCID: PMC3839059
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.22077
Genomic location analysis by ChIP-Seq
Abstract
The interaction of a multitude of transcription factors and other chromatin proteins with the genome can influence gene expression and subsequently cell differentiation and function. Thus systematic identification of binding targets of transcription factors is key to unraveling gene regulation networks. The recent development of ChIP-Seq has revolutionized mapping of DNA-protein interactions. Now protein binding can be mapped in a truly genome-wide manner with extremely high resolution. This review discusses ChIP-Seq technology, its possible pitfalls, data analysis and several early applications.
Figures
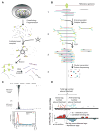
References
-
- Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z, Wei G, Chepelev I, Zhao K. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell. 2007a;129:823–37. - PubMed
-
- Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z, Wei G, Chepelev I, Zhao K. Response: Mapping Nucleosome Positions Using ChIP-Seq Data. Cell. 2007b;131:832–33.
-
- Bernstein BE, Meissner A, Lander ES. The mammalian epigenome. Cell. 2007;128:669–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

