A novel DNA-binding protein modulating methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 19173709
- PMCID: PMC2658668
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-15
A novel DNA-binding protein modulating methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
Background: Methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus is conferred by the mecA-encoded penicillin-binding protein PBP2a. Additional genomic factors are also known to influence resistance levels in strain specific ways, although little is known about their contribution to resistance phenotypes in clinical isolates. Here we searched for novel proteins binding to the mec operator, in an attempt to identify new factor(s) controlling methicillin resistance phenotypes.
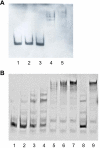
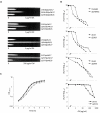
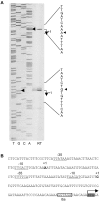
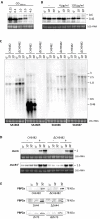
Results: Analysis of proteins binding to a DNA fragment containing the mec operator region identified a novel, putative helix-turn-helix DNA-binding protein, SA1665. Nonpolar deletion of SA1665, in heterogeneously methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA) of different genetic backgrounds, increased methicillin resistance levels in a strain dependent manner. This phenotype could be fully complemented by reintroducing SA1665 in trans. Northern and Western blot analyses, however, revealed that SA1665 had no visible influence on mecA transcription or amounts of PBP2a produced.
Conclusion: SA1665 is a new chromosomal factor which influences methicillin resistance in MRSA. Although SA1665 bound to the mecA promoter region, it had no apparent influence on mecA transcription or translation, suggesting that this predicted DNA-binding protein modulates resistance indirectly, most likely through the control of other genomic factors which contribute to resistance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of mecA transcriptional regulation in the phenotypic expression of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 1996 Sep;178(18):5464-71. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.18.5464-5471.1996. J Bacteriol. 1996. PMID: 8808937 Free PMC article.
-
Eagle-type methicillin resistance: new phenotype of high methicillin resistance under mec regulator gene control.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001 Mar;45(3):815-24. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.3.815-824.2001. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001. PMID: 11181367 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of mec regulator genes in clinical methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates according to the production of coagulase, types of enterotoxin, and toxic shock syndrome toxin-1.Hiroshima J Med Sci. 1999 Jun;48(2):49-56. Hiroshima J Med Sci. 1999. PMID: 10434474
-
Molecular aspects of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus.J Antimicrob Chemother. 1994 Jan;33(1):7-24. doi: 10.1093/jac/33.1.7. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1994. PMID: 8157576 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus.Microbiologia. 1997 Sep;13(3):301-8. Microbiologia. 1997. PMID: 9353748 Review.
Cited by
-
Heteroresistance to fosfomycin is predominant in Streptococcus pneumoniae and depends on the murA1 gene.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Jun;57(6):2801-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00223-13. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23571543 Free PMC article.
-
The Novel Streptococcal Transcriptional Regulator XtgS Negatively Regulates Bacterial Virulence and Directly Represses PseP Transcription.Infect Immun. 2020 Sep 18;88(10):e00035-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00035-20. Print 2020 Sep 18. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32690636 Free PMC article.
-
New shuttle vector-based expression system to generate polyhistidine-tagged fusion proteins in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 May 1;81(9):3243-54. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03803-14. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25747000 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of thioridazine resistance in Staphylococcus aureus.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 8;13(8):e0201767. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201767. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30089175 Free PMC article.
-
A low-affinity penicillin-binding protein 2x variant is required for heteroresistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Jul;58(7):3934-41. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02547-14. Epub 2014 Apr 28. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24777105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lim D, Strynadka NC. Structural basis for the β-lactam resistance of PBP2a from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Nat Struct Biol. 2002;9(11):870–876. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

