Primary hepatic carcinoid tumor: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 19173727
- PMCID: PMC2654436
- DOI: 10.1186/1757-1626-2-90
Primary hepatic carcinoid tumor: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Primary hepatic carcinoid tumor (PHCT) is very rare and difficult to diagnose before biopsy or operation. We report a patient with a small PHCT and review cases in the literature.
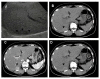
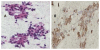
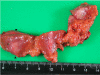
Case presentation: A 48-year-old Chinese female with underlying hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection was found to have a low echoic hepatic nodule by abdominal ultrasound. Tumor markers were negative. Dynamic liver computed tomography scans showed enhancement of the nodule in the arterial phase and early washout in the portal phase. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was considered based on the image findings and underlying HBV infection. However, the tumor biopsy revealed a malignant neoplasm that originating from neuroendocrine cells. Pre-operative and intra-operative investigations for the possible other origin of carcinoid tumor were negative, so PHCT was confirmed.
Conclusion: A small and asymptomatic PHCT is extremely rare. PHCT should be one of the differential diagnoses in patients with small hepatic tumor, even in regions with high prevalence of HBV infection and HCC. Pre-operative biopsy is necessary to avoid misdiagnosis even when HCC is highly suspected clinically.
Figures
References
-
- Edmondson. H. Tumor of the liver and intrahepatic bile duct. Atlas of tumor pathology, section 7, fascicle 25 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Washington, DC. 1958. pp. 105–9.
-
- Sano K, Kosuge T, Yamamoto J. Primary hepatic carcinoid tumors confirmed with long-term follow-up after resection. Hepato-gastroenterology. 1999;46(28):2547–50. - PubMed
-
- Iwao M, Nakamuta M, Enjoji M. Primary hepatic carcinoid tumor: case report and review of 53 cases. Med Sci Monit. 2001;7(4):746–50. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

