Profiling RE1/REST-mediated histone modifications in the human genome
- PMID: 19173732
- PMCID: PMC2687797
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2009-10-1-r9
Profiling RE1/REST-mediated histone modifications in the human genome
Abstract
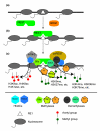
Background: The transcriptional repressor REST (RE1 silencing transcription factor, also called NRSF for neuron-restrictive silencing factor) binds to a conserved RE1 motif and represses many neuronal genes in non-neuronal cells. This transcriptional regulation is transacted by several nucleosome-modifying enzymes recruited by REST to RE1 sites, including histone deacetylases (for example, HDAC1/2), demethylases (for example, LSD1), and methyltransferases (for example, G9a).
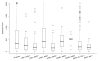
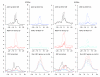
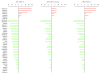
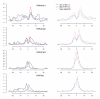
Results: We have investigated a panel of 38 histone modifications by ChIP-Seq analysis for REST-mediated changes. Our study reveals a systematic decline of histone acetylations modulated by the association of RE1 with REST (RE1/REST). By contrast, alteration of histone methylations is more heterogeneous, with some methylations increased (for example, H3K27me3, and H3K9me2/3) and others decreased (for example, H3K4me, and H3K9me1). Furthermore, the observation of such trends of histone modifications in upregulated genes demonstrates convincingly that these changes are not determined by gene expression but are RE1/REST dependent. The outcomes of REST binding to canonical and non-canonical RE1 sites were nearly identical. Our analyses have also provided the first direct evidence that REST induces context-specific nucleosome repositioning, and furthermore demonstrate that REST-mediated histone modifications correlate with the affinity of RE1 motifs and the abundance of RE1-bound REST molecules.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that the landscape of REST-mediated chromatin remodeling is dynamic and complex, with novel histone modifying enzymes and mechanisms yet to be elucidated. Our results should provide valuable insights for selecting the most informative histone marks for investigating the mechanisms and the consequences of REST modulated nucleosome remodeling in both neural and non-neural systems.
Figures



References
-
- Scholl T, Stevens MB, Mahanta S, Strominger JL. A zinc finger protein that represses transcription of the human MHC class II gene, DPA. J Immunol. 1996;156:1448–1457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

