Impact of interleukin-6 on hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension and lung inflammation in mice
- PMID: 19173740
- PMCID: PMC2644669
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-10-6
Impact of interleukin-6 on hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension and lung inflammation in mice
Abstract
Background: Inflammation may contribute to the pathogenesis of various forms of pulmonary hypertension (PH). Recent studies in patients with idiopathic PH or PH associated with underlying diseases suggest a role for interleukin-6 (IL-6).
Methods: To determine whether endogenous IL-6 contributes to mediate hypoxic PH and lung inflammation, we studied IL-6-deficient (IL-6-/-) and wild-type (IL-6+/+) mice exposed to hypoxia for 2 weeks.
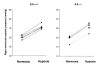
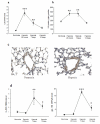
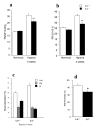
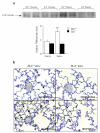
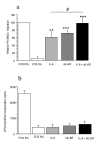
Results: Right ventricular systolic pressure, right ventricle hypertrophy, and the number and media thickness of muscular pulmonary vessels were decreased in IL-6-/- mice compared to wild-type controls after 2 weeks' hypoxia, although the pressure response to acute hypoxia was similar in IL-6+/+ and IL-6-/- mice. Hypoxia exposure of IL-6+/+ mice led to marked increases in IL-6 mRNA and protein levels within the first week, with positive IL-6 immunostaining in the pulmonary vessel walls. Lung IL-6 receptor and gp 130 (the IL-6 signal transducer) mRNA levels increased after 1 and 2 weeks' hypoxia. In vitro studies of cultured human pulmonary-artery smooth-muscle-cells (PA-SMCs) and microvascular endothelial cells revealed prominent synthesis of IL-6 by PA-SMCs, with further stimulation by hypoxia. IL-6 also markedly stimulated PA-SMC migration without affecting proliferation. Hypoxic IL-6-/- mice showed less inflammatory cell recruitment in the lungs, compared to hypoxic wild-type mice, as assessed by lung protein levels and immunostaining for the specific macrophage marker F4/80, with no difference in lung expression of adhesion molecules or cytokines.
Conclusion: These data suggest that IL-6 may be actively involved in hypoxia-induced lung inflammation and pulmonary vascular remodeling in mice.
Figures
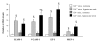
References
-
- Peinado VI, Barbera JA, Abate P, Ramirez J, Roca J, Santos S, Rodriguez-Roisin R. Inflammatory reaction in pulmonary muscular arteries of patients with mild chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;159(5 Pt 1):1605–1611. - PubMed
-
- Humbert M, Monti G, Brenot F, Sitbon O, Portier A, Grangeot-Keros L, Duroux P, Galanaud P, Simonneau G, Emilie D. Increased interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 serum concentrations in severe primary pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;151(5):1628–1631. - PubMed
-
- Balabanian K, Foussat A, Dorfmuller P, Durand-Gasselin I, Capel F, Bouchet-Delbos L, Portier A, Marfaing-Koka A, Krzysiek R, Rimaniol AC, et al. CX(3)C chemokine fractalkine in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165(10):1419–1425. doi: 10.1164/rccm.2106007. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

