VEGF-mediated disruption of endothelial CLN-5 promotes blood-brain barrier breakdown
- PMID: 19174516
- PMCID: PMC2644149
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0808698106
VEGF-mediated disruption of endothelial CLN-5 promotes blood-brain barrier breakdown
Abstract
Breakdown of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) is an early and significant event in CNS inflammation. Astrocyte-derived VEGF-A has been implicated in this response, but the underlying mechanisms remain unresolved. Here, we identify the endothelial transmembrane tight junction proteins claudin-5 (CLN-5) and occludin (OCLN) as targets of VEGF-A action. Down-regulation of CLN-5 and OCLN accompanied up-regulation of VEGF-A and correlated with BBB breakdown in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, an animal model of CNS inflammatory disease. In cultures of brain microvascular endothelial cells, VEGF-A specifically down-regulated CLN-5 and OCLN protein and mRNA. In mouse cerebral cortex, microinjection of VEGF-A disrupted CLN-5 and OCLN and induced loss of barrier function. Importantly, functional studies revealed that expression of recombinant CLN-5 protected brain microvascular endothelial cell cultures from a VEGF-induced increase in paracellular permeability, whereas recombinant OCLN expressed under the same promoter was not protective. Previous studies have shown CLN-5 to be a key determinant of trans-endothelial resistance at the BBB. Our findings suggest that its down-regulation by VEGF-A constitutes a significant mechanism in BBB breakdown.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
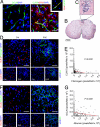
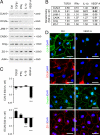
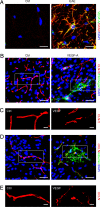
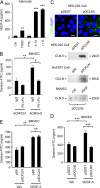
References
-
- Zlokovic BV. The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron. 2008;57:178–201. - PubMed
-
- Abbott NJ, Rönnbäck L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood- brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:41–53. - PubMed
-
- Tsukita S, Furuse M. Claudin-based barrier in simple and stratified cellular sheets. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002;14:531–536. - PubMed
-
- Ohtsuki S, et al. Exogenous expression of claudin-5 induces barrier properties in cultured rat brain capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 2007;210:81–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

