Involvement of the vitamin D receptor in energy metabolism: regulation of uncoupling proteins
- PMID: 19176352
- PMCID: PMC2670625
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.90763.2008
Involvement of the vitamin D receptor in energy metabolism: regulation of uncoupling proteins
Abstract
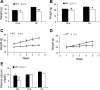
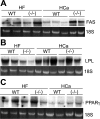
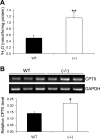
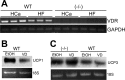
Recent studies have established that vitamin D plays multiple biological roles beyond calcium metabolism; however, whether vitamin D is involved in energy metabolism is unknown. To address this question, we characterized the metabolic phenotypes of vitamin D receptor (VDR)-null mutant mice. Under a normocalcemic condition, VDR-null mice displayed less body fat mass and lower plasma triglyceride and cholesterol levels compared with wild-type (WT) mice; when placed on a high-fat diet, VDR-null mice showed a slower growth rate and accumulated less fat mass globally than WT mice, even though their food intake and intestinal lipid transport capacity were the same as WT mice. Consistent with the lower adipose mass, plasma leptin levels were lower and white adipocytes were histologically smaller in VDR-null mice than WT mice. The rate of fatty acid beta-oxidation in the white adipose tissue was higher, and the expression of uncoupling protein (UCP) 1, UCP2 and UCP3 was markedly upregulated in VDR-null mice, suggesting a higher energy expenditure in the mutant mice. Experiments using primary brown fat culture confirmed that 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 directly suppressed the expression of the UCPs. Consistently, the energy expenditure, oxygen consumption, and CO2 production in VDR-null mice were markedly higher than in WT mice. These data indicate that vitamin D is involved in energy metabolism and adipocyte biology in vivo in part through regulation of beta-oxidation and UCP expression.
Figures




References
-
- Alonso M, Goodwin C, Liao X, Page D, Refetoff S, Weiss RE. Effects of maternal levels of thyroid hormone (TH) on the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid set point: studies in TH receptor beta knockout mice. Endocrinology 148: 5305–5312, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Miyagawa J, Hotta K, Shimomura I, Nakamura T, Miyaoka K, Kuriyama H, Nishida M, Yamashita S, Okubo K, Matsubara K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 257: 79–83, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Arsenijevic D, Onuma H, Pecqueur C, Raimbault S, Manning BS, Miroux B, Couplan E, Alves-Guerra MC, Goubern M, Surwit R, Bouillaud F, Richard D, Collins S, Ricquier D. Disruption of the uncoupling protein-2 gene in mice reveals a role in immunity and reactive oxygen species production. Nat Genet 26: 435–439, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Asturias FJ, Chadick JZ, Cheung IK, Stark H, Witkowski A, Joshi AK, Smith S. Structure and molecular organization of mammalian fatty acid synthase. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12: 225–232, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Barnea M, Shamay A, Stark AH, Madar Z. A high-fat diet has a tissue-specific effect on adiponectin and related enzyme expression. Obesity (Silver Spring) 14: 2145–2153, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

