Suppression of cFLIP by lupeol, a dietary triterpene, is sufficient to overcome resistance to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in chemoresistant human pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 19176377
- PMCID: PMC2996261
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2917
Suppression of cFLIP by lupeol, a dietary triterpene, is sufficient to overcome resistance to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in chemoresistant human pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
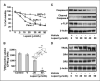
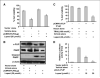
Overexpression of cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein (cFLIP) is reported to confer chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer (PaC) cells. This study was designed to investigate the effect of lupeol, a dietary triterpene, on (a) apoptosis of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) therapy-resistant PaC cells overexpressing cFLIP and (b) growth of human pancreatic tumor xenografts in vivo. The effect of lupeol treatment on proliferation and TRAIL/caspase-8/cFLIP machinery in PaC cells was investigated. Next, cFLIP-overexpressing and cFLIP-suppressed cells were tested for sensitivity to recombinant TRAIL therapy in the presence of lupeol. Further, athymic nude mice implanted with AsPC-1 cells were treated with lupeol (40 mg/kg) thrice a week and surrogate biomarkers were evaluated in tumors. Lupeol alone treatment of cells caused (a) decrease in proliferation, (b) induction of caspase-8 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage, and (c) down-regulation of transcriptional activation and expression of cFLIP. Lupeol was observed to increase the TRAIL protein level in cells. Lupeol significantly decreased the viability of AsPC-1 cells both in cFLIP-suppressed cells and in cFLIP-overexpressing cells. Lupeol significantly sensitized chemoresistant PaC cells to undergo apoptosis by recombinant TRAIL. Finally, lupeol significantly reduced the growth of human PaC tumors propagated in athymic nude mice and caused modulation of cFLIP and TRAIL protein levels in tumors. Our findings showed the anticancer efficacy of lupeol with mechanistic rationale against highly chemoresistant human PaC cells. We suggest that lupeol, alone or as an adjuvant to current therapies, could be useful for the management of human PaC.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Lupeol triterpene, a novel diet-based microtubule targeting agent: disrupts survivin/cFLIP activation in prostate cancer cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Oct 23;388(3):576-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.08.060. Epub 2009 Aug 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19683515 Free PMC article.
-
Co-treatment of birinapant with TRAIL synergistically induces apoptosis by downregulating cFLIP(L) in MDA-MB-453 cell lines.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Dec 10;533(3):289-295. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.09.031. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32958259
-
Growth inhibition and apoptosis induced by lupeol, a dietary triterpene, in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(4):517-22. doi: 10.1248/bpb.34.517. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011. PMID: 21467639
-
Lupeol inhibits growth of highly aggressive human metastatic melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo by inducing apoptosis.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Apr 1;14(7):2119-27. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4413. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18381953
-
Lupeol, a novel anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer dietary triterpene.Cancer Lett. 2009 Nov 28;285(2):109-15. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.04.033. Epub 2009 May 22. Cancer Lett. 2009. PMID: 19464787 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dandelion root extract affects colorectal cancer proliferation and survival through the activation of multiple death signalling pathways.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 8;7(45):73080-73100. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11485. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27564258 Free PMC article.
-
Preparative scale extraction of mangiferin and lupeol from mango (Mangifera indica L.) leaves and bark by different extraction methods.J Food Sci Technol. 2019 Oct;56(10):4625-4631. doi: 10.1007/s13197-019-03909-0. Epub 2019 Jul 8. J Food Sci Technol. 2019. PMID: 31686694 Free PMC article.
-
20-Hydroxy-3-Oxolupan-28-Oic Acid, a Minor Component From Mahonia bealei (Fort.) Carr. Leaves Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory in Murine Macrophages.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Jun 17;9:701876. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.701876. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34222220 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of MADD and c-FLIP overcomes resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2011 Oct;205(4):362.e12-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2011.05.035. Epub 2011 May 27. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2011. PMID: 21855847 Free PMC article.
-
Lupeol alters viability of SK-RC-45 (Renal cell carcinoma cell line) by modulating its mitochondrial dynamics.Heliyon. 2019 Aug 2;5(8):e02107. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02107. eCollection 2019 Aug. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31417967 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Garcea G, Dennison AR, Pattenden CJ, Neal CP, Sutton CD, Berry DP. Survival following curative resection for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. A systematic review of the literature. JOP. 2008;9:99–132. - PubMed
-
- Mimeault M, Brand RE, Sasson AA, Batra SK. Recent advances on the molecular mechanisms involved in pancreatic cancer progression and therapies. Pancreas. 2005;31:301–16. - PubMed
-
- Xiong HQ. Molecular targeting therapy for pancreatic cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2004;54:69–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

