Non-cleavage site gag mutations in amprenavir-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) predispose HIV-1 to rapid acquisition of amprenavir resistance but delay development of resistance to other protease inhibitors
- PMID: 19176623
- PMCID: PMC2655547
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02539-08
Non-cleavage site gag mutations in amprenavir-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) predispose HIV-1 to rapid acquisition of amprenavir resistance but delay development of resistance to other protease inhibitors
Abstract
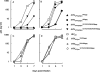
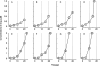
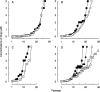
In an attempt to determine whether mutations in Gag in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) variants selected with a protease inhibitor (PI) affect the development of resistance to the same or a different PI(s), we generated multiple infectious HIV-1 clones carrying mutated Gag and/or mutated protease proteins that were identified in amprenavir (APV)-selected HIV-1 variants and examined their virological characteristics. In an HIV-1 preparation selected with APV (33 passages, yielding HIV(APVp33)), we identified six mutations in protease and six apparently critical mutations at cleavage and non-cleavage sites in Gag. An infectious recombinant clone carrying the six protease mutations but no Gag mutations failed to replicate, indicating that the Gag mutations were required for the replication of HIV(APVp33). An infectious recombinant clone that carried wild-type protease and a set of five Gag mutations (rHIV(WTpro)(12/75/219/390/409gag)) replicated comparably to wild-type HIV-1; however, when exposed to APV, rHIV(WTpro)(12/75/219/390/409gag) rapidly acquired APV resistance. In contrast, the five Gag mutations significantly delayed the acquisition of HIV-1 resistance to ritonavir and nelfinavir (NFV). Recombinant HIV-1 clones containing NFV resistance-associated mutations, such as D30N and N88S, had increased susceptibilities to APV, suggesting that antiretroviral regimens including both APV and NFV may bring about favorable antiviral efficacy. The present data suggest that the preexistence of certain Gag mutations related to PI resistance can accelerate the emergence of resistance to the PI and delay the acquisition of HIV resistance to other PIs, and these findings should have clinical relevance in the therapy of HIV-1 infection with PI-including regimens.
Figures

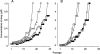

References
-
- Amano, M., Y. Koh, D. Das, J. Li, S. Leschenko, Y. F. Wang, P. I. Boross, I. T. Weber, A. K. Ghosh, and H. Mitsuya. 2007. A novel bis-tetrahydrofuranylurethane-containing nonpeptidic protease inhibitor (PI), GRL-98065, is potent against multiple-PI-resistant human immunodeficiency virus in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 512143-2155. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bally, F., R. Martinez, S. Peters, P. Sudre, and A. Telenti. 2000. Polymorphism of HIV type 1 gag p7/p1 and p1/p6 cleavage sites: clinical significance and implications for resistance to protease inhibitors. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 161209-1213. - PubMed
-
- Bhaskaran, K., O. Hamouda, M. Sannes, F. Boufassa, A. M. Johnson, P. C. Lambert, and K. Porter. 2008. Changes in the risk of death after HIV seroconversion compared with mortality in the general population. JAMA 30051-59. - PubMed
-
- Carrillo, A., K. D. Stewart, H. L. Sham, D. W. Norbeck, W. E. Kohlbrenner, J. M. Leonard, D. J. Kempf, and A. Molla. 1998. In vitro selection and characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 variants with increased resistance to ABT-378, a novel protease inhibitor. J. Virol. 727532-7541. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

