Rapid activation of plasticity-associated gene transcription in hippocampal neurons provides a mechanism for encoding of one-trial experience
- PMID: 19176799
- PMCID: PMC2749324
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4588-08.2009
Rapid activation of plasticity-associated gene transcription in hippocampal neurons provides a mechanism for encoding of one-trial experience
Abstract
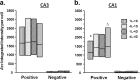
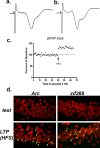
The hippocampus is hypothesized to support rapid encoding of ongoing experience. A critical prerequisite for such function is the ability to readily recruit enduring synaptic plasticity in hippocampal neurons. Hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) and memory consolidation require expression of the immediate-early gene (IEG) Arc. To determine whether Arc transcription could be driven by limited and controlled behavioral experience, we used a rectangular track paradigm. In past electrophysiological studies, pyramidal neurons recorded from rats running in one direction on similar tracks typically exhibited a single firing field. Using fluorescence in situ hybridization, we show that the behavioral activity associated with a single lap around the track was sufficient to trigger Arc transcription in complete CA3 neuronal ensembles, as predicted given the role of CA3 in one-trial learning. In contrast, Arc transcription in CA1 ensembles was recruited incrementally, with maximal activation achieved after four laps a day for 4 consecutive days. To test whether Arc transcription is linked to learning and plasticity, or merely elicited by location-specific firing, we inactivated the medial septum, a treatment that compromises hippocampus-dependent learning and LTP but spares location-specific firing in CA1 neurons. Septal inactivation abolished track training-induced Arc transcription in CA1 and CA3 neurons, showing that Arc transcription requires plasticity-inducing stimuli. Accordingly, LTP induction activated Arc transcription in CA1 neurons in vivo. These findings demonstrate for the first time that a single brief experience, equivalent to a single crossing of a firing field, can trigger IEG expression required for long-term plasticity in the hippocampus.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Experience-dependent gene expression in the rat hippocampus after spatial learning: a comparison of the immediate-early genes Arc, c-fos, and zif268.J Neurosci. 2001 Jul 15;21(14):5089-98. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-14-05089.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11438584 Free PMC article.
-
Subfield-specific immediate early gene expression associated with hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo.Eur J Neurosci. 2001 Mar;13(5):968-76. doi: 10.1046/j.0953-816x.2001.01467.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11264669
-
Temporal dynamics of Arc gene induction in hippocampus: relationship to context memory formation.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2012 Mar;97(3):313-20. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2012.02.004. Epub 2012 Feb 27. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2012. PMID: 22390855
-
The immediate early gene arc/arg3.1: regulation, mechanisms, and function.J Neurosci. 2008 Nov 12;28(46):11760-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3864-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19005037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arc ubiquitination in synaptic plasticity.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018 May;77:10-16. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.09.009. Epub 2017 Sep 7. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 28890418 Review.
Cited by
-
Contextual memory engrams, and the neuromodulatory influence of the locus coeruleus.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Feb 5;17:1342622. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1342622. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38375501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of DNA Methylation Impairs Synaptic Plasticity during an Early Time Window in Rats.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:4783836. doi: 10.1155/2016/4783836. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 27493805 Free PMC article.
-
Time determines the neural circuit underlying associative fear learning.Front Behav Neurosci. 2011 Dec 27;5:89. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2011.00089. eCollection 2011. Front Behav Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22207842 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct roles for dorsal CA3 and CA1 in memory for sequential nonspatial events.Learn Mem. 2009 Dec 22;17(1):12-17. doi: 10.1101/lm.1616209. Print 2010 Jan. Learn Mem. 2009. PMID: 20028733 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional memory impairments in a genetic rat model of depression: involvement of 5-HT/MEK/Arc signaling in restoration.Mol Psychiatry. 2012 Feb;17(2):173-84. doi: 10.1038/mp.2010.131. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Mol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 21242991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham WC, Dragunow M, Tate WP. The role of immediate early genes in the stabilization of long-term potentiation. Mol Neurobiol. 1991;5:297–314. - PubMed
-
- Acsády L, Káli S. Models, structure, function: the transformation of cortical signals in the dentate gyrus. Prog Brain Res. 2007;163:577–599. - PubMed
-
- Bozon B, Davis S, Laroche S. Regulated transcription of the immediate-early gene Zif268: mechanisms and gene dosage-dependent function in synaptic plasticity and memory formation. Hippocampus. 2002;12:570–577. - PubMed
-
- Buzsáki G. Theta oscillations in the hippocampus. Neuron. 2002;33:325–340. - PubMed
-
- Chawla MK, Lin G, Olson K, Vazdarjanova A, Burke SN, McNaughton BL, Worley PF, Guzowski JF, Roysam B, Barnes CA. 3D-catFISH: a system for automated quantitative three-dimensional compartmental analysis of temporal gene transcription activity imaged by fluorescence in situ hybridization. J Neurosci Methods. 2004;139:13–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
