Glomeruli of Dense Deposit Disease contain components of the alternative and terminal complement pathway
- PMID: 19177158
- PMCID: PMC2738640
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2008.657
Glomeruli of Dense Deposit Disease contain components of the alternative and terminal complement pathway
Abstract
Dense Deposit Disease (DDD), or membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis type II, is a rare renal disease characterized by dense deposits in the mesangium and along the glomerular basement membranes that can be seen by electron microscopy. Although these deposits contain complement factor C3, as determined by immunofluorescence microscopy, their precise composition remains unknown. To address this question, we used mass spectrometry to identify the proteins in laser microdissected glomeruli isolated from paraffin-embedded tissue of eight confirmed cases of DDD. Compared to glomeruli from five control patients, we found that all of the glomeruli from patients with DDD contain components of the alternative pathway and terminal complement complex. Factor C9 was uniformly present as well as the two fluid-phase regulators of terminal complement complex clusterin and vitronectin. In contrast, in nine patients with immune complex-mediated membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, glomerular samples contained mainly immunoglobulins and complement factors C3 and C4. Our study shows that in addition to fluid-phase dysregulation of the alternative pathway, soluble components of the terminal complement complex contribute to glomerular lesions found in DDD.
Figures
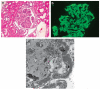




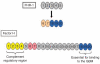
Comment in
-
Tissue proteomics: a new investigative tool for renal biopsy analysis.Kidney Int. 2009 May;75(9):876-9. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.54. Kidney Int. 2009. PMID: 19367311
References
-
- Appel GB, Cook HT, Hageman G, et al. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis type II (dense deposit disease): an update. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:1392–1403. - PubMed
-
- Pickering MC, Cook HT, Warren J, et al. Uncontrolled C3 activation causes membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis in mice deficient in complement factor H. Nat Genet. 2002;31:424–428. - PubMed
-
- Licht C, Heinen S, Jozsi M, et al. Deletion of Lys224 in regulatory domain 4 of factor H reveals a novel pathomechanism for dense deposit disease (MPGN II) Kidney Int. 2006;70:42–50. - PubMed
-
- Schwertz R, Rother U, Anders D, et al. Complement analysis in children with idiopathic membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis: a long-term follow-up. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2001;12:166–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

