The future of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) in metabolic profiling and metabolomic studies for biomarker discovery
- PMID: 19177179
- PMCID: PMC2631423
- DOI: 10.2217/17520363.1.1.159
The future of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) in metabolic profiling and metabolomic studies for biomarker discovery
Abstract
The future utility of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) in metabolic profiling and metabolomic studies for biomarker discover will be discussed, beginning with a brief description of the evolution of metabolomics and the utilization of the three most popular analytical platforms in such studies: NMR, GC-MS, and LC-MS. Emphasis is placed on recent developments in high-efficiency LC separations, sensitive electrospray ionization approaches, and the benefits to incorporating both in LC-MS-based approaches. The advantages and disadvantages of various quantitative approaches are reviewed, followed by the current LC-MS-based tools available for candidate biomarker characterization and identification. Finally, a brief prediction on the future path of LC-MS-based methods in metabolic profiling and metabolomic studies is given.
Figures
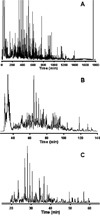

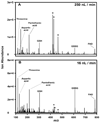
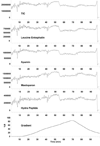
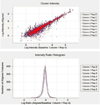

References
-
- Nicholson JK, Lindon JC, Holmes E. 'Metabonomics': understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica. 1999;29:1181–1189. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson JK, Connelly J, Lindon JC, Holmes E. Metabonomics: a platform for studying drug toxicity and gene function. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002;1:153–161. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson JK, Wilson ID. Understanding 'global' systems biology: metabonomicsand the continuum of metabolism. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003;2:668–676. - PubMed
-
- Lindon JC, Holmes E, Nicholson JK. So what's the deal with metabonomics? Anal. Biochem. 2003;75:384A–391A. - PubMed
-
- Pauling L. Orthomolecular psychiatry: varying the concentrations of substances normally present in the human body may control mental disease. Science. 1968;160:265–271. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
