Crystal structures of the X-domains of a Group-1 and a Group-3 coronavirus reveal that ADP-ribose-binding may not be a conserved property
- PMID: 19177346
- PMCID: PMC2708038
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.15
Crystal structures of the X-domains of a Group-1 and a Group-3 coronavirus reveal that ADP-ribose-binding may not be a conserved property
Abstract
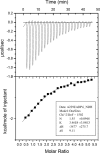
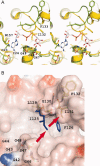
The polyproteins of coronaviruses are cleaved by viral proteases into at least 15 nonstructural proteins (Nsps). Consisting of five domains, Nsp3 is the largest of these (180-210 kDa). Among these domains, the so-called X-domain is believed to act as ADP-ribose-1''-phosphate phosphatase or to bind poly(ADP-ribose). However, here we show that the X-domain of Infectious Bronchitis Virus (strain Beaudette), a Group-3 coronavirus, fails to bind ADP-ribose. This is explained on the basis of the crystal structure of the protein, determined at two different pH values. For comparison, we also describe the crystal structure of the homologous X-domain from Human Coronavirus 229E, a Group-1 coronavirus, which does bind ADP-ribose.
Figures

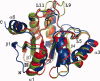
Similar articles
-
The SARS-unique domain (SUD) of SARS coronavirus contains two macrodomains that bind G-quadruplexes.PLoS Pathog. 2009 May;5(5):e1000428. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000428. Epub 2009 May 15. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19436709 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of two coronavirus ADP-ribose-1''-monophosphatases and their complexes with ADP-Ribose: a systematic structural analysis of the viral ADRP domain.J Virol. 2009 Jan;83(2):1083-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01862-08. Epub 2008 Nov 5. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 18987156 Free PMC article.
-
The ADP-ribose-1''-monophosphatase domains of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and human coronavirus 229E mediate resistance to antiviral interferon responses.J Gen Virol. 2011 Aug;92(Pt 8):1899-1905. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.031856-0. Epub 2011 Apr 27. J Gen Virol. 2011. PMID: 21525212
-
Players in ADP-ribosylation: Readers and Erasers.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2016;17(7):654-667. doi: 10.2174/1389203717666160419144846. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2016. PMID: 27090904 Review.
-
Nsp3 of coronaviruses: Structures and functions of a large multi-domain protein.Antiviral Res. 2018 Jan;149:58-74. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.11.001. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Antiviral Res. 2018. PMID: 29128390 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The VIZIER project: overview; expectations; and achievements.Antiviral Res. 2010 Aug;87(2):85-94. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2010.02.326. Epub 2010 Mar 10. Antiviral Res. 2010. PMID: 20226212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatics and functional analyses of coronavirus nonstructural proteins involved in the formation of replicative organelles.Antiviral Res. 2016 Nov;135:97-107. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.10.005. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Antiviral Res. 2016. PMID: 27743916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SARS-unique domain (SUD) of SARS coronavirus contains two macrodomains that bind G-quadruplexes.PLoS Pathog. 2009 May;5(5):e1000428. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000428. Epub 2009 May 15. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19436709 Free PMC article.
-
The macro domain as fusion tag for carrier-driven crystallization.Protein Sci. 2017 Feb;26(2):365-374. doi: 10.1002/pro.3073. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Protein Sci. 2017. PMID: 27774698 Free PMC article.
-
Drug similarity and structure-based screening of medicinal compounds to target macrodomain-I from SARS-CoV-2 to rescue the host immune system: a molecular dynamics study.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022 Jan;40(1):523-537. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1815583. Epub 2020 Sep 8. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 32897173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cavanagh D. Coronavirus avian infectious bronchitis virus. Vet Res. 2007;38:281–297. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

