R-Spondin1 protects mice from chemotherapy or radiation-induced oral mucositis through the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin pathway
- PMID: 19179402
- PMCID: PMC2650156
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0805159106
R-Spondin1 protects mice from chemotherapy or radiation-induced oral mucositis through the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin pathway
Abstract
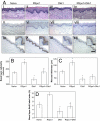
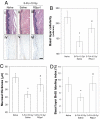
R-Spondin1 (RSpo1) is a novel secreted protein that augments canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. We injected recombinant RSpo1 protein into transgenic Wnt reporter TOPGAL mice and have identified the oral mucosa as a target tissue for RSpo1. Administration of RSpo1 into normal mice triggered nuclear translocation of beta-catenin and resulted in increased basal layer cellularity, thickened mucosa, and elevated epithelial cell proliferation in tongue. We herein evaluated the therapeutic potential of RSpo1 in treating chemotherapy or radiotherapy-induced oral mucositis in several mouse models. Prophylactic treatment with RSpo1 dose-dependently overcame the reduction of basal layer epithelial cellularity, mucosal thickness, and epithelial cell proliferation in tongues of mice exposed to whole-body irradiation. RSpo1 administration also substantially alleviated tongue mucositis in the oral cavity of mice receiving concomitant 5-fluorouracil and x-ray radiation. Furthermore, RSpo1 significantly reduced the extent of tongue ulceration in mice receiving a single fraction, high dose head-only radiation in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, combined therapy of RSpo1 and keratinocyte growth factor resulted in complete healing of tongue ulcers in mice subjected to snout-only irradiation. In conclusion, our results demonstrate RSpo1 to be a potent therapeutic agent for oral mucositis by enhancing basal layer epithelial regeneration and accelerating mucosal repair through up-regulation of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

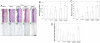

References
-
- Kim KA, et al. R-Spondin proteins: A novel link to beta-catenin activation. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:23–26. - PubMed
-
- Nam JS, Turcotte TJ, Smith PF, Choi S, Yoon JK. Mouse cristin/R-spondin family proteins are novel ligands for the Frizzled 8 and LRP6 receptors and activate beta-catenin-dependent gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:13247–13257. - PubMed
-
- Wei Q, et al. R-spondin1 is a high affinity ligand for LRP6 and induces LRP6 phosphorylation and beta-catenin signaling. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:15903–15911. - PubMed
-
- Kamata T, et al. R-spondin, a novel gene with thrombospondin type 1 domain, was expressed in the dorsal neural tube and affected in Wnts mutants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1676:51–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

