Galectin-3 is critical for the development of the allergic inflammatory response in a mouse model of atopic dermatitis
- PMID: 19179612
- PMCID: PMC2665752
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080500
Galectin-3 is critical for the development of the allergic inflammatory response in a mouse model of atopic dermatitis
Abstract
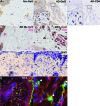
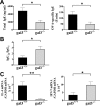
Galectin-3 belongs to a family of beta-galactoside-binding animal lectins expressed in several cell types, including epithelial and immune cells. To establish the role of galectin-3 in the development of allergic skin inflammation, we compared inflammatory skin responses of galectin-3-deficient (gal3(-/-)) and wild-type (gal3(+/+)) mice to epicutaneous sensitization with ovalbumin (OVA). OVA-treated gal3(-/-) mice exhibited markedly reduced epidermal thickening, lower eosinophil infiltration, and lower serum IgE levels compared with gal3(+/+) mice. The former evoked lower interleukin-4, but higher interferon-gamma, mRNA expression at OVA-treated skin sites. Moreover, gal3(-/-) splenocytes from OVA-sensitized mice secreted more interleukin-12 compared with gal3(+/+) splenocytes. In addition, antigen presentation by gal3(-/-) dendritic cells to T cells in vitro were T helper cell (Th1)-polarized relative to presentation by gal3(+/+) dendritic cells. When exposed to OVA, recipients engrafted with T cells from gal3(-/-) OVA-specific T cell receptor transgenic mice developed significantly reduced dermatitis and a markedly lower Th2 response compared with recipients of comparable gal3(+/+) T cells. We conclude that galectin-3 is critical for the development of inflammatory Th2 responses to epicutaneously administered antigens; in its absence, mice develop a Th1-polarized response. This regulatory effect of galectin-3 on Th development is exerted at both the dendritic cell and T cell levels. Our studies suggest that galectin-3 may play an important role in the acute phase of human atopic dermatitis.
Figures
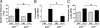


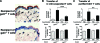
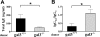
Similar articles
-
Critical role for galectin-3 in airway inflammation and bronchial hyperresponsiveness in a murine model of asthma.Am J Pathol. 2004 Dec;165(6):2045-53. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63255-5. Am J Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15579447 Free PMC article.
-
IL-22 promotes allergic airway inflammation in epicutaneously sensitized mice.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Feb;143(2):619-630.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.05.032. Epub 2018 Jun 18. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 29920352 Free PMC article.
-
CD19 expression in B cells regulates atopic dermatitis in a mouse model.Am J Pathol. 2013 Jun;182(6):2214-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.02.042. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Am J Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23583649 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-3 and the skin.J Dermatol Sci. 2011 Nov;64(2):85-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2011.07.008. Epub 2011 Aug 11. J Dermatol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21889881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of Galectin-3 in autoimmunity and tumor progression.Immunol Res. 2012 Apr;52(1-2):100-10. doi: 10.1007/s12026-012-8286-6. Immunol Res. 2012. PMID: 22418727 Review.
Cited by
-
N-Glycosylation and Inflammation; the Not-So-Sweet Relation.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 27;13:893365. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.893365. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35833138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A non-synonymous polymorphism in galectin-3 lectin domain is associated with allergic reactions to beta-lactam antibiotics.Pharmacogenomics J. 2016 Feb;16(1):79-82. doi: 10.1038/tpj.2015.24. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Pharmacogenomics J. 2016. PMID: 25869013
-
Galectin-3 impacts Cryptococcus neoformans infection through direct antifungal effects.Nat Commun. 2017 Dec 6;8(1):1968. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02126-7. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29213074 Free PMC article.
-
High Expression of Galectin-3 in Patients with IgG4-Related Disease: A Proteomic Approach.Patholog Res Int. 2017;2017:9312142. doi: 10.1155/2017/9312142. Epub 2017 May 16. Patholog Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28593065 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-3 Inhibits Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Growth and Impacts Paracoccidioidomycosis through Multiple Mechanisms.mSphere. 2019 Apr 24;4(2):e00209-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00209-19. mSphere. 2019. PMID: 31019001 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grewe M, Bruijnzeel-Koomen CA, Schopf E, Thepen T, Langeveld-Wildschut AG, Ruzicka T, Krutmann J. A role for Th1 and Th2 cells in the immunopathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Immunol Today. 1998;19:359–361. - PubMed
-
- Leffler H, Carlsson S, Hedlund M, Qian Y, Poirier F. Introduction to galectins. Glycoconj J. 2004;19:433–440. - PubMed
-
- Kasai K, Hirabayashi J. Galectins: a family of animal lectins that decipher glycocodes. J Biochem (Tokyo) 1996;119:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Liu FT. Regulatory roles of galectins in the immune response. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2005;136:385–400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

