Delineating the signals by which repetitive deformation stimulates intestinal epithelial migration across fibronectin
- PMID: 19179620
- PMCID: PMC2670672
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.90648.2008
Delineating the signals by which repetitive deformation stimulates intestinal epithelial migration across fibronectin
Abstract
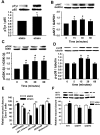
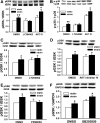
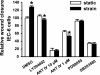
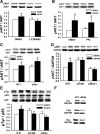
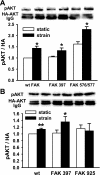
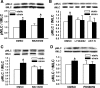
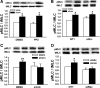
Repetitive strain stimulates intestinal epithelial migration across fibronectin via focal adhesion kinase (FAK), Src, and extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) although how these signals act and interact remains unclear. We hypothesized that PI3K is central to this pathway. We subjected Caco-2 and intestinal epithelial cell-6 cells to 10 cycles/min deformation on flexible fibronectin-coated membranes, assayed migration by wound closure, and signaling by immunoblots. Strain stimulated PI3K, AKT, glycogen synthase kinase (GSK), and p38 phosphorylation. Blocking each kinase prevented strain stimulation of migration. Blocking PI3K prevented strain-stimulated ERK and p38 phosphorylation. Blocking AKT did not. Downstream, blocking PI3K, AKT, or ERK inhibited strain-induced GSK-Ser9 phosphorylation. Upstream of AKT, reducing FAK or Rac1 by siRNA blocked strain-stimulated AKT phosphorylation, but inhibiting Src by PP2 or siRNA did not. Transfection with FAK point mutants at Tyr397, Tyr576/577, or Tyr925 demonstrated that only FAK925 phosphorylation is required for strain-stimulated AKT phosphorylation. Myosin light chain activation by strain required FAK, Rac1, PI3K, AKT, GSK, and ERK but not Src or p38. Finally, blebbistatin, a nonmuscle myosin II inhibitor, blocked the motogenic effect of strain downstream of myosin light chain. Thus strain stimulates intestinal epithelial migration across fibronectin by a complex pathway including Src, FAK, Rac1, PI3K, AKT, GSK, ERK, p38, myosin light chain, and myosin II.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ILK mediates the effects of strain on intestinal epithelial wound closure.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Feb;300(2):C356-67. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00273.2010. Epub 2010 Nov 17. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21084641 Free PMC article.
-
Role of RhoA and its effectors ROCK and mDia1 in the modulation of deformation-induced FAK, ERK, p38, and MLC motogenic signals in human Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Nov;301(5):C1224-38. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00518.2010. Epub 2011 Aug 17. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21849669 Free PMC article.
-
Repetitive deformation activates Src-independent FAK-dependent ERK motogenic signals in human Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008 Jun;294(6):C1350-61. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00027.2008. Epub 2008 Apr 9. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18400991 Free PMC article.
-
Repetitive deformation activates focal adhesion kinase and ERK mitogenic signals in human Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells through Src and Rac1.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jan 5;282(1):14-28. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605817200. Epub 2006 Nov 6. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17088251
-
Cordycepin and kinase inhibition in cancer.Drug Discov Today. 2023 Mar;28(3):103481. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2022.103481. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Drug Discov Today. 2023. PMID: 36584876 Review.
Cited by
-
ILK mediates the effects of strain on intestinal epithelial wound closure.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Feb;300(2):C356-67. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00273.2010. Epub 2010 Nov 17. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21084641 Free PMC article.
-
Transglutaminase-2 in cell adhesion: all roads lead to paxillin?Cell Adh Migr. 2013 Sep-Oct;7(5):412-7. doi: 10.4161/cam.26344. Epub 2013 Sep 12. Cell Adh Migr. 2013. PMID: 24193434 Free PMC article.
-
Fluid flow and guidance of collective cell migration.Cell Adh Migr. 2010 Jul-Sep;4(3):353-7. doi: 10.4161/cam.4.3.11428. Cell Adh Migr. 2010. PMID: 20234192 Free PMC article.
-
Role of RhoA and its effectors ROCK and mDia1 in the modulation of deformation-induced FAK, ERK, p38, and MLC motogenic signals in human Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Nov;301(5):C1224-38. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00518.2010. Epub 2011 Aug 17. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21849669 Free PMC article.
-
Schlafen 12 mediates the effects of butyrate and repetitive mechanical deformation on intestinal epithelial differentiation in human Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells.Hum Cell. 2019 Jul;32(3):240-250. doi: 10.1007/s13577-019-00247-3. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Hum Cell. 2019. PMID: 30875077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Jurf AS, Younoszai MK, Chapman-Furr F. Effect of nutritional method on adaptation of the intestinal remnant after massive bowel resection. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 4: 245–252, 1985. - PubMed
-
- Alahari SK Nischarin inhibits Rac induced migration and invasion of epithelial cells by affecting signaling cascades involving PAK. Exp Cell Res 288: 415–424, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Amin MA, Ruth JH, Haas CS, Pakozdi A, Mansfield PJ, Haghshenas J, Koch AE. H-2g, a glucose analog of blood group H antigen, mediates mononuclear cell recruitment via Src and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathways. Arthritis Rheum 58: 689–695, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Antico G, Lingen MW, Sassano A, Melby J, Welch RW, Fiore S, Pilon AL, Miele L. Recombinant human uteroglobin/CC10 inhibits the adhesion and migration of primary human endothelial cells via specific and saturable binding to fibronectin. J Cell Physiol 207: 553–561, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

