Knocking down barriers: advances in siRNA delivery
- PMID: 19180106
- PMCID: PMC7097568
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd2742
Knocking down barriers: advances in siRNA delivery
Erratum in
- Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009 Jun;8(6):516
Abstract
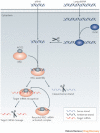
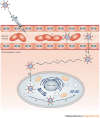
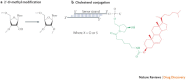
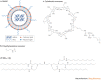
In the 10 years that have passed since the Nobel prize-winning discovery of RNA interference (RNAi), billions of dollars have been invested in the therapeutic application of gene silencing in humans. Today, there are promising data from ongoing clinical trials for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration and respiratory syncytial virus. Despite these early successes, however, the widespread use of RNAi therapeutics for disease prevention and treatment requires the development of clinically suitable, safe and effective drug delivery vehicles. Here, we provide an update on the progress of RNAi therapeutics and highlight novel synthetic materials for the encapsulation and intracellular delivery of nucleic acids.
Figures
References
-
- Fire A, et al. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
-
- Elbashir SM, et al. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 2001;411:494–498. - PubMed
-
- McCaffrey AP, et al. Gene expression: RNA interference in adult mice. Nature. 2002;418:38–39. - PubMed
-
- Morrissey DV, et al. Potent and persistent in vivo anti-HBV activity of chemically modified siRNAs. Nature Biotech. 2005;23:1002–1007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

