Increased expression of the Akt/PKB inhibitor TRB3 in osteoarthritic chondrocytes inhibits insulin-like growth factor 1-mediated cell survival and proteoglycan synthesis
- PMID: 19180501
- PMCID: PMC2637941
- DOI: 10.1002/art.24225
Increased expression of the Akt/PKB inhibitor TRB3 in osteoarthritic chondrocytes inhibits insulin-like growth factor 1-mediated cell survival and proteoglycan synthesis
Abstract
Objective: The chondrocyte response to insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) is reduced with aging and in osteoarthritis (OA). IGF-1 signals through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. TRB3, a tribbles homolog, has been shown to inhibit IGF-1-mediated activation of Akt in HEK 293 cells. This study was undertaken to determine if TRB3 is expressed in chondrocytes, and whether the chondrocyte response to IGF-1 is reduced by TRB3.
Methods: Human articular cartilage was obtained from normal tissue donors and from patients with OA at the time of knee replacement surgery. TRB3 was assessed in the tissue samples by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, immunoblotting, and immunohistochemistry. Overexpression of TRB3 was induced by transient transfection to determine the effects of TRB3 on cell survival and proteoglycan synthesis.
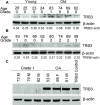
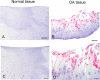
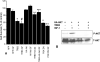
Results: TRB3 messenger RNA was detected in normal human chondrocytes. TRB3 protein levels were low in cells from normal cartilage but significantly increased in cells from OA cartilage. Incubation with 2 agents that induce endoplasmic reticulum stress, tunicamycin and thapsigargin, increased TRB3 levels in normal cells. Overexpression of TRB3 inhibited Akt phosphorylation and reduced chondrocyte survival and proteoglycan synthesis.
Conclusion: These results are the first to demonstrate that TRB3 is present in human chondrocytes, and that the level of TRB3 is increased in OA cartilage and in isolated OA chondrocytes. Because it is an inhibitor of Akt activation, elevated TRB3 production could play a role in the increased cell death and reduced response to IGF-1 observed in OA cartilage.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Oxidative stress inhibits insulin-like growth factor-I induction of chondrocyte proteoglycan synthesis through differential regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase-Akt and MEK-ERK MAPK signaling pathways.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 13;284(46):31972-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.056838. Epub 2009 Sep 17. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19762915 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT/visfatin) inhibits insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling and proteoglycan synthesis in human articular chondrocytes.Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 Jan 30;14(1):R23. doi: 10.1186/ar3705. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 22289259 Free PMC article.
-
TRB3 overexpression due to endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibits AKT kinase activation of tongue squamous cell carcinoma.Oral Oncol. 2011 Oct;47(10):934-9. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2011.06.512. Epub 2011 Aug 6. Oral Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21821462
-
The combination of insulin-like growth factor 1 and osteogenic protein 1 promotes increased survival of and matrix synthesis by normal and osteoarthritic human articular chondrocytes.Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Aug;48(8):2188-96. doi: 10.1002/art.11209. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. PMID: 12905472
-
ADAM-12 (meltrin alpha) is involved in chondrocyte proliferation via cleavage of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 in osteoarthritic cartilage.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Mar;58(3):778-89. doi: 10.1002/art.23262. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18311789
Cited by
-
Insights into the underlying pathogenesis and therapeutic potential of endoplasmic reticulum stress in degenerative musculoskeletal diseases.Mil Med Res. 2023 Nov 9;10(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s40779-023-00485-5. Mil Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37941072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian Tribbles homolog 3 impairs insulin action in skeletal muscle: role in glucose-induced insulin resistance.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Mar;298(3):E565-76. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00467.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 8. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 19996382 Free PMC article.
-
Low back pain and osteoarthritis pain: a perspective of estrogen.Bone Res. 2023 Aug 4;11(1):42. doi: 10.1038/s41413-023-00280-x. Bone Res. 2023. PMID: 37542028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Recovery of Cognitive and Affective Deficiencies Linked with Chronic Osteoarthritis Pain and Implicated Pathways by Slow-Releasing Hydrogen Sulfide Treatment.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Oct 16;10(10):1632. doi: 10.3390/antiox10101632. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34679766 Free PMC article.
-
Kindlin-2 Promotes Chondrogenesis and Ameliorates IL-1beta-Induced Inflammation in Chondrocytes Cocultured with BMSCs in the Direct Contact Coculture System.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Apr 12;2022:3156245. doi: 10.1155/2022/3156245. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35450413 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aigner T, Haag J, Martin J, Buckwalter J. Osteoarthritis: aging of matrix and cells - going for a remedy. Current Drug Targets. 2007;8:325–331. - PubMed
-
- Goldring MB. The role of the chondrocyte in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43(9):1916–26. - PubMed
-
- Loeser RF, Shanker G, Carlson CS, Gardin JF, Shelton BJ, Sonntag WE. Reduction in the chondrocyte response to insulin-like growth factor 1 in aging and osteoarthritis: studies in a non-human primate model of naturally occurring disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43(9):2110–20. - PubMed
-
- van Osch GJ, van den Berg WB, Hunziker EB, Hauselmann HJ. Differential effects of IGF-1 and TGF beta-2 on the assembly of proteoglycans in pericellular and territorial matrix by cultured bovine articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1998;6(3):187–95. - PubMed
-
- Guenther HL, Guenther HE, Froesch ER, Fleisch H. Effect of insulin-like growth factor on collagen and glycosaminoglycan synthesis by rabbit articular chondrocytes in culture. Experientia. 1982;38(8):979–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

