In vitro characterization of the enzyme properties of the phospholipid N-methyltransferase PmtA from Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- PMID: 19181804
- PMCID: PMC2655499
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01591-08
In vitro characterization of the enzyme properties of the phospholipid N-methyltransferase PmtA from Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Abstract
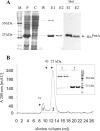
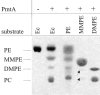
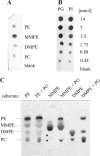
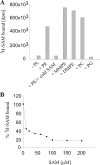
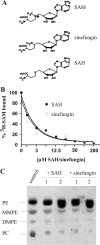
Agrobacterium tumefaciens requires phosphatidylcholine (PC) in its membranes for plant infection. The phospholipid N-methyltransferase PmtA catalyzes all three transmethylation reactions of phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) to PC via the intermediates monomethylphosphatidylethanolamine (MMPE) and dimethylphosphatidylethanolamine (DMPE). The enzyme uses S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) as the methyl donor, converting it to S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH). Little is known about the activity of bacterial Pmt enzymes, since PC biosynthesis in prokaryotes is rare. In this article, we present the purification and in vitro characterization of A. tumefaciens PmtA, which is a monomeric protein. It binds to PE, the intermediates MMPE and DMPE, the end product PC, and phosphatidylglycerol (PG) and phosphatidylinositol. Binding of the phospholipid substrates precedes binding of SAM. We used a coupled in vitro assay system to demonstrate the enzymatic activity of PmtA and to show that PmtA is inhibited by the end products PC and SAH and the antibiotic sinefungin. The presence of PG stimulates PmtA activity. Our study provides insights into the catalysis and control of a bacterial phospholipid N-methyltransferase.
Figures

References
-
- Arondel, V., C. Benning, and C. R. Somerville. 1993. Isolation and functional expression in Escherichia coli of a gene encoding phosphatidylethanolamine methyltransferase (EC 2.1.1.17) from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J. Biol. Chem. 26816002-16008. - PubMed
-
- Bligh, E. G., and W. J. Dyer. 1959. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37911-917. - PubMed
-
- Carman, G. M., R. A. Deems, and E. A. Dennis. 1995. Lipid signaling enzymes and surface dilution kinetics. J. Biol. Chem. 27018711-18714. - PubMed
-
- Cho, W., and R. V. Stahelin. 2005. Membrane-protein interactions in cell signaling and membrane trafficking. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 34119-151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

