Massively parallel sequencing of the polyadenylated transcriptome of C. elegans
- PMID: 19181841
- PMCID: PMC2665784
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.088112.108
Massively parallel sequencing of the polyadenylated transcriptome of C. elegans
Abstract
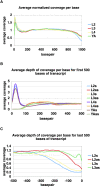
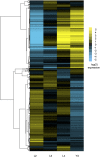
Using massively parallel sequencing by synthesis methods, we have surveyed the polyA+ transcripts from four stages of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans to an unprecedented depth. Using novel statistical approaches, we evaluated the coverage of annotated features of the genome and of candidate processed transcripts, including splice junctions, trans-spliced leader sequences, and polyadenylation tracts. The data provide experimental support for >85% of the annotated protein-coding transcripts in WormBase (WS170) and confirm additional details of processing. For example, the total number of confirmed splice junctions was raised from 70,911 to over 98,000. The data also suggest thousands of modifications to WormBase annotations and identify new spliced junctions and genes not part of any WormBase annotation, including at least 80 putative genes not found in any of three predicted gene sets. The quantitative nature of the data also suggests that mRNA levels may be measured by this approach with unparalleled precision. Although most sequences align with protein-coding genes, a small fraction falls in introns and intergenic regions. One notable region on the X chromosome encodes a noncoding transcript of >10 kb localized to somatic nuclei.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Formation, regulation and evolution of Caenorhabditis elegans 3'UTRs.Nature. 2011 Jan 6;469(7328):97-101. doi: 10.1038/nature09616. Epub 2010 Nov 17. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21085120 Free PMC article.
-
The tpa-1 gene of Caenorhabditis elegans encodes two proteins similar to Ca(2+)-independent protein kinase Cs: evidence by complete genomic and complementary DNA sequences of the tpa-1 gene.J Mol Biol. 1995 Aug 25;251(4):477-85. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0449. J Mol Biol. 1995. PMID: 7658466
-
Teamed up for transcription.Nature. 2002 Jun 20;417(6891):797-8. doi: 10.1038/417797a. Nature. 2002. PMID: 12075329 No abstract available.
-
Overview of gene structure.WormBook. 2006 Jan 18:1-10. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.65.1. WormBook. 2006. PMID: 18023127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA processing in C. elegans.Methods Cell Biol. 2011;106:187-217. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-544172-8.00007-4. Methods Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 22118278 Review.
Cited by
-
Visualization and dissemination of multidimensional proteomics data comparing protein abundance during Caenorhabditis elegans development.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2015 Nov;26(11):1827-36. doi: 10.1007/s13361-015-1193-z. Epub 2015 Jul 2. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2015. PMID: 26133526 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) by paired-end RNA sequencing.DNA Res. 2012 Apr;19(2):131-42. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsr046. Epub 2012 Jan 24. DNA Res. 2012. PMID: 22279088 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphorylation patterns in Caenorhabditis elegans operons, polycistronic gene clusters with only one promoter.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;30(15):3887-93. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00325-10. Epub 2010 May 24. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20498277 Free PMC article.
-
De novo characterization of Larix gmelinii (Rupr.) Rupr. transcriptome and analysis of its gene expression induced by jasmonates.BMC Genomics. 2013 Aug 13;14:548. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-548. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23941306 Free PMC article.
-
Data in support of genome-wide identification of lineage-specific genes within Caenorhabditis elegans.Data Brief. 2015 Aug 3;4:595-601. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2015.07.032. eCollection 2015 Sep. Data Brief. 2015. PMID: 26442285 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baugh L.R., Hill A.A., Slonim D.K., Brown E.L., Hunter C.P. Composition and dynamics of the Caenorhabditis elegans early embryonic transcriptome. Development. 2003;130:889–900. - PubMed
-
- The C. elegans Genome Sequencing Consortium. Genome sequence of the nematode C. elegans: A platform for investigating biology. Science. 1998;282:2012–2018. - PubMed
-
- Cloonan N., Forrest A.R., Kolle G., Gardiner B.B., Faulkner G.J., Brown M.K., Taylor D.F., Steptoe A.L., Wani S., Bethel G., et al. Stem cell transcriptome profiling via massive-scale mRNA sequencing. Nat. Methods. 2008;5:613–619. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
