Protection from lethal gram-negative bacterial sepsis by targeting Toll-like receptor 4
- PMID: 19181857
- PMCID: PMC2650125
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0808146106
Protection from lethal gram-negative bacterial sepsis by targeting Toll-like receptor 4
Abstract
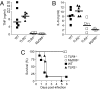
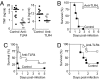
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), the signal-transducing molecule of the LPS receptor complex, plays a fundamental role in the sensing of LPS from gram-negative bacteria. Activation of TLR4 signaling pathways by LPS is a critical upstream event in the pathogenesis of gram-negative sepsis, making TLR4 an attractive target for novel antisepsis therapy. To validate the concept of TLR4-targeted treatment strategies in gram-negative sepsis, we first showed that TLR4(-/-) and myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88 (MyD88)(-/-) mice were fully resistant to Escherichia coli-induced septic shock, whereas TLR2(-/-) and wild-type mice rapidly died of fulminant sepsis. Neutralizing anti-TLR4 antibodies were then generated using a soluble chimeric fusion protein composed of the N-terminal domain of mouse TLR4 (amino acids 1-334) and the Fc portion of human IgG1. Anti-TLR4 antibodies inhibited intracellular signaling, markedly reduced cytokine production, and protected mice from lethal endotoxic shock and E. coli sepsis when administered in a prophylactic and therapeutic manner up to 13 h after the onset of bacterial sepsis. These experimental data provide strong support for the concept of TLR4-targeted therapy for gram-negative sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
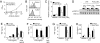

References
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1546–1554. - PubMed
-
- Russell JA. Management of sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1699–1713. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B, Rietschel ET. Innate immune sensing and its roots: The story of endotoxin. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:169–176. - PubMed
-
- Hoshino KO, et al. Cutting edge: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-deficient mice are hyporesponsive to lipopolysaccharide: evidence for TLR4 as the Lps gene product. J Immunol. 1999;162:3749–3752. - PubMed
-
- Poltorak A, et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: Mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science. 1998;282:2085–2088. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

