Ephrin-B3 reverse signaling through Grb4 and cytoskeletal regulators mediates axon pruning
- PMID: 19182796
- PMCID: PMC2661084
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2254
Ephrin-B3 reverse signaling through Grb4 and cytoskeletal regulators mediates axon pruning
Abstract
It has been suggested that ephrin-B proteins have receptor-like roles in the control of axon pathfinding by repulsion, although it is largely unknown how the reverse signals are coupled to downstream intracellular molecules and how they induce cytoskeletal reorganization at the axon terminal. We found that ephrin-B3 (EB3) was able to function as a repulsive guidance receptor and mediate stereotyped pruning of murine hippocampal mossy fiber axons during postnatal development. Targeted intracellular point mutants showed that axon pruning requires tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent reverse signaling and coupling to the SH2/SH3 adaptor protein Grb4 (also known as Nckbeta/Nck2). Furthermore, we found that the second SH3 domain of Grb4 is required and sufficient for axon pruning/retraction by mediating interactions with Dock180 and PAK to bring about guanine nucleotide exchange and signaling downstream of Rac, respectively. Our results reveal a previously unknown pathway that controls axon pruning and elucidate the biochemical mechanism by which ephrin-B reverse signals regulate actin dynamics to bring about the retraction of growth cones.
Figures
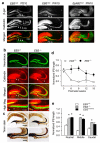
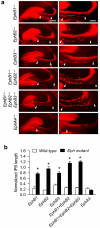
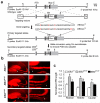
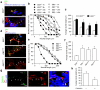


References
-
- Patel BN, Van Vactor DL. Axon guidance: the cytoplasmic tail. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002;14:221–229. - PubMed
-
- Guan KL, Rao Y. Signalling mechanisms mediating neuronal responses to guidance cues. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4:941–956. - PubMed
-
- Huber AB, Kolodkin AL, Ginty DD, Cloutier JF. Signaling at the growth cone: ligand-receptor complexes and the control of axon growth and guidance. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2003;26:509–563. - PubMed
-
- Luo L, O'Leary DD. Axon retraction and degeneration in development and disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2005;28:127–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

