Differential chromatin marking of introns and expressed exons by H3K36me3
- PMID: 19182803
- PMCID: PMC2648722
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.322
Differential chromatin marking of introns and expressed exons by H3K36me3
Abstract
Variation in patterns of methylations of histone tails reflects and modulates chromatin structure and function. To provide a framework for the analysis of chromatin function in Caenorhabditis elegans, we generated a genome-wide map of histone H3 tail methylations. We find that C. elegans genes show distributions of histone modifications that are similar to those of other organisms, with H3K4me3 near transcription start sites, H3K36me3 in the body of genes and H3K9me3 enriched on silent genes. We also observe a novel pattern: exons are preferentially marked with H3K36me3 relative to introns. H3K36me3 exon marking is dependent on transcription and is found at lower levels in alternatively spliced exons, supporting a splicing-related marking mechanism. We further show that the difference in H3K36me3 marking between exons and introns is evolutionarily conserved in human and mouse. We propose that H3K36me3 exon marking in chromatin provides a dynamic link between transcription and splicing.
Figures
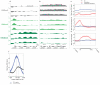
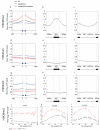

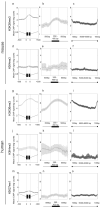
Comment in
-
Processing the H3K36me3 signature.Nat Genet. 2009 Mar;41(3):270-1. doi: 10.1038/ng0309-270. Nat Genet. 2009. PMID: 19240748 No abstract available.
References
-
- Berger SL. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature. 2007;447:407–12. - PubMed
-
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 2007;128:693–705. - PubMed
-
- Shilatifard A. Chromatin modifications by methylation and ubiquitination: implications in the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:243–69. - PubMed
-
- Consortium C.e.S. Genome sequence of the nematode C. elegans: a platform for investigating biology. The C. elegans Sequencing Consortium. Science. 1998;282:2012–8. - PubMed
-
- Fire A, et al. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

