Alpha-synuclein is part of a diverse and highly conserved interaction network that includes PARK9 and manganese toxicity
- PMID: 19182805
- PMCID: PMC2683786
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.300
Alpha-synuclein is part of a diverse and highly conserved interaction network that includes PARK9 and manganese toxicity
Abstract
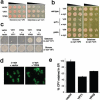
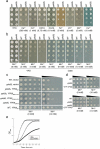
Parkinson's disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies and multiple system atrophy, collectively referred to as synucleinopathies, are associated with a diverse group of genetic and environmental susceptibilities. The best studied of these is PD. alpha-Synuclein (alpha-syn) has a key role in the pathogenesis of both familial and sporadic PD, but evidence linking it to other predisposition factors is limited. Here we report a strong genetic interaction between alpha-syn and the yeast ortholog of the PD-linked gene ATP13A2 (also known as PARK9). Dopaminergic neuron loss caused by alpha-syn overexpression in animal and neuronal PD models is rescued by coexpression of PARK9. Further, knockdown of the ATP13A2 ortholog in Caenorhabditis elegans enhances alpha-syn misfolding. These data provide a direct functional connection between alpha-syn and another PD susceptibility locus. Manganese exposure is an environmental risk factor linked to PD and PD-like syndromes. We discovered that yeast PARK9 helps to protect cells from manganese toxicity, revealing a connection between PD genetics (alpha-syn and PARK9) and an environmental risk factor (PARK9 and manganese). Finally, we show that additional genes from our yeast screen, with diverse functions, are potent modifiers of alpha-syn-induced neuron loss in animals, establishing a diverse, highly conserved interaction network for alpha-syn.
Figures
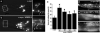


References
-
- Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Mechanisms of Parkinson's disease linked to pathological alpha-synuclein: new targets for drug discovery. Neuron. 2006;52:33–8. - PubMed
-
- Chartier-Harlin MC, et al. Alpha-synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 2004;364:1167–9. - PubMed
-
- Ibanez P, et al. Causal relation between alpha-synuclein gene duplication and familial Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 2004;364:1169–71. - PubMed
-
- Singleton AB, et al. alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson's disease. Science. 2003;302:841. - PubMed
-
- Spillantini MG, et al. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature. 1997;388:839–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

