The interleukin 23 receptor is essential for the terminal differentiation of interleukin 17-producing effector T helper cells in vivo
- PMID: 19182808
- PMCID: PMC2945605
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1698
The interleukin 23 receptor is essential for the terminal differentiation of interleukin 17-producing effector T helper cells in vivo
Abstract
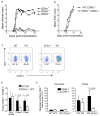
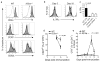
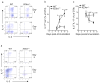
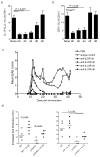
Interleukin 23 (IL-23) is required for autoimmune inflammation mediated by IL-17-producing helper T cells (T(H)-17 cells) and has been linked to many human immune disorders. Here we restricted deficiency in the IL-23 receptor to defined cell populations in vivo to investigate the requirement for IL-23 signaling in the development and function of T(H)-17 cells in autoimmunity, inflammation and infection. In the absence of IL-23, T(H)-17 development was stalled at the early activation stage. T(H)-17 cells failed to downregulate IL-2 and also failed to maintain IL-17 production or upregulate expression of the IL-7 receptor alpha-chain. These defects were associated with less proliferation; consequently, fewer effector T(H)-17 cells were produced in the lymph nodes and hence available to emigrate to the bloodstream and tissues.
Figures



Comment in
-
Don't leave home without it: the IL-23 visa to T(H)-17 cells.Nat Immunol. 2009 Mar;10(3):236-8. doi: 10.1038/ni0309-236. Nat Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19221553 No abstract available.
References
-
- Oppmann B, et al. Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity. 2000;13:715–25. - PubMed
-
- Cua DJ, et al. Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nature. 2003;421:744–8. - PubMed
-
- McKenzie BS, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ. Understanding the IL-23–IL-17 immune pathway. Trends Immunol. 2006;27:17–23. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

