Isolation of mammalian 26S proteasomes and p97/VCP complexes using the ubiquitin-like domain from HHR23B reveals novel proteasome-associated proteins
- PMID: 19182904
- PMCID: PMC3811022
- DOI: 10.1021/bi802198q
Isolation of mammalian 26S proteasomes and p97/VCP complexes using the ubiquitin-like domain from HHR23B reveals novel proteasome-associated proteins
Abstract
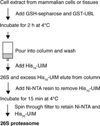
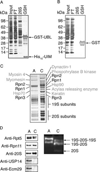
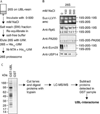
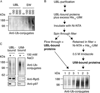
Recent studies, mainly in yeast, have identified various cofactors that associate with the 26S proteasome and appear to influence its function. To identify these proteins in different cells and physiological states, we developed a method to gently and rapidly isolate 26S proteasomes and associated proteins without the need for genetic modifications of the proteasome. This method is based on the affinity of this complex for the ubiquitin-like (UBL) domain of hHR23B and elution with a competing polypeptide containing a ubiquitin-interacting motif. Associated with 26S proteasomes from rat muscle were a variety of known proteasome-interacting proteins, activators, and ubiquitin conjugates. In addition, we identified over 40 proteins not previously known to associate with the 26S proteasome, some of which were tightly associated with the proteasome in a substoichiometric fashion, e.g., the deubiquitinating enzymes USP5/isopeptidase T and USP7/HAUSP and the ubiquitin ligases ARF-BP1/HUWE1 and p600/UBR4. By altering buffer conditions, we also purified by this approach complexes of the ATPase p97/VCP associated with its adaptor proteins Ufd1-Npl4, p47, SAKS1, and FAF1, all of which contain ubiquitin-binding motifs. These complexes were isolated with ubiquitin conjugates bound and were not previously known to bind to the UBL domain of hHR23B. These various UBL-interacting proteins, dubbed the UBL interactome, represent a network of proteins that function together in ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis, and the UBL method offers many advantages for studies of the diversity, functions, and regulation of 26S proteasomes and p97 complexes under different conditions.
Figures


References
-
- Ciechanover A. Proteolysis: from the lysosome to ubiquitin and the proteasome. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005;6:79–87. - PubMed
-
- Smith DM, Benaroudj N, Goldberg A. Proteasomes and their associated ATPases: a destructive combination. J. Struct. Biol. 2006;156:72–83. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt M, Hanna J, Elsasser S, Finley D. Proteasome-associated proteins: regulation of a proteolytic machine. Biol. Chem. 2005;386:725–737. - PubMed
-
- Glickman MH, Raveh D. Proteasome plasticity. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:3214–3223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

