Chemoselectivity: the mother of invention in total synthesis
- PMID: 19182997
- PMCID: PMC2765532
- DOI: 10.1021/ar800182r
Chemoselectivity: the mother of invention in total synthesis
Abstract
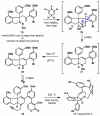
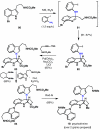
IUPAC defines chemoselectivity as "the preferential reaction of a chemical reagent with one of two or more different functional groups", a definition that describes in rather understated terms the single greatest obstacle to complex molecule synthesis. Indeed, efforts to synthesize natural products often become case studies in the art and science of chemoselective control, a skill that nature has practiced deftly for billions of years but man has yet to master. Confrontation of one or perhaps a collection of functional groups that are either promiscuously reactive or stubbornly inert has the potential to unravel an entire strategic design. One could argue that the degree to which chemists can control chemoselectivity pales in comparison to the state of the art in stereocontrol. In this Account, we hope to illustrate how the combination of necessity and tenacity leads to the invention of chemoselective chemistry for the construction of complex molecules. In our laboratory, a premium is placed upon selecting targets that would be difficult or impossible to synthesize using traditional techniques. The successful total synthesis of such molecules demands a high degree of innovation, which in turn enables the discovery of new reactivity and principles for controlling chemoselectivity. In devising an approach to a difficult target, we choose bond disconnections that primarily maximize skeletal simplification, especially when the proposed chemistry is poorly precedented or completely unknown. By choosing such a strategy--rather than adapting an approach to fit known reactions--innovation and invention become the primary goal of the total synthesis. Delivery of the target molecule in a concise and convergent manner is the natural consequence of such endeavors, and invention becomes a prerequisite for success.
Figures

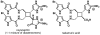
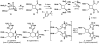
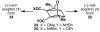


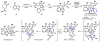

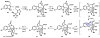
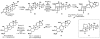
References
-
- Baran PS, Maimone TJ, Richter JM. Total Synthesis of Marine Natural Products Without Using Protecting Groups. Nature. 2007;446:404–408. - PubMed
-
-
The word “Chemoselectivity” and the challenges in designing reactions that are chemoselective were first pointed out by Trost in 1973, see Trost BM, Salzmann TN. New Synthetic Reactions. Sulfenylation-Dehydrosulfenylation as a Method for Introduction of Unsaturation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1973;95:6840–6842. For a detailed discussion, see Trost BM. Selectivity: A Key to Synthetic Efficiency. Science. 1983;219:245–250.
-
-
-
For a review on the isolation, biosynthesis, and synthetic studies of dimeric pyrrole-imidazole alkaloids, see Kock M, Grube A, Seiple I, Baran PS. The Pursuit of Palau'amine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007;46:6586–6594. and references therein.
-
-
- Baran PS, Li K, O'Malley DP, Mitsos C. Short, Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Sceptrin and Ageliferin by Programmed Oxaquadricyclane Fragmentation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006;45:249–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

