Effects of alcohol on performance on a distraction task during simulated driving
- PMID: 19183133
- PMCID: PMC2753192
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00876.x
Effects of alcohol on performance on a distraction task during simulated driving
Abstract
Background: Prior studies report that accidents involving intoxicated drivers are more likely to occur during performance of secondary tasks. We studied this phenomenon, using a dual-task paradigm, involving performance of a visual oddball (VO) task while driving in an alcohol challenge paradigm. Previous functional MRI (fMRI) studies of the VO task have shown activation in the anterior cingulate, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex. Thus, we predicted dose-dependent decreases in activation of these areas during VO performance.
Methods: Forty healthy social drinkers were administered 3 different doses of alcohol, individually tailored to their gender and weight. Participants performed a VO task while operating a virtual reality driving simulator in a 3T fMRI scanner.
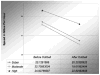
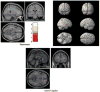
Results: Analysis showed a dose-dependent linear decrease in Blood Oxygen Level Dependent activation during task performance, primarily in hippocampus, anterior cingulate, and dorsolateral prefrontal areas, with the least activation occurring during the high dose. Behavioral analysis showed a dose-dependent linear increase in reaction time, with no effects associated with either correct hits or false alarms. In all dose conditions, driving speed decreased significantly after a VO stimulus. However, at the high dose this decrease was significantly less. Passenger-side line crossings significantly increased at the high dose.
Conclusions: These results suggest that driving impairment during secondary task performance may be associated with alcohol-related effects on the above brain regions, which are involved with attentional processing/decision-making. Drivers with high blood alcohol concentrations may be less able to orient or detect novel or sudden stimuli during driving.
Figures

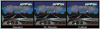


References
-
- Ardekani B, Choi S, Hossein-Zadeh G, Porjesz B, Tanabe J, Lim K, Bilder R, Helpern J, Begleiter H. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of brain activity in the visual oddball task. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res. 2002;14:347–356. - PubMed
-
- Babor T, Higgins-Biddle J, Saunders J, Moneiro M. Department of Mental Health and Substance Dependence. World Health Organization; Geneva Switzerland: 2001. Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test: Guidelines for Use in Primary Care.
-
- Benar C, Schon D, Grimault S, Nazarian B, Burle B, Roth M, Badier J, Marquis P, Liegeois-Chauvel C, Anton J. Single-trial analysis of oddball event-related potentials in simultaneous EEG-fMRI. Hum Brain Mapp. 2007;28:602–613. - PubMed
-
- Brazdil M, Mikl M, Marecek R, Krupa P, Rektor I. Effective connectivity in target stimulus processing: a dynamic causal modeling study of visual oddball task. NeuroImage. 2007;35:827–835. - PubMed
-
- Brewer N, Sandow B. Alcohol effects on driver performance under conditions of divided attention. Ergonomics. 1980;23:185–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

