Thyroid hormone beta receptor activation has additive cholesterol lowering activity in combination with atorvastatin in rabbits, dogs and monkeys
- PMID: 19183199
- PMCID: PMC2697679
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2009.00038.x
Thyroid hormone beta receptor activation has additive cholesterol lowering activity in combination with atorvastatin in rabbits, dogs and monkeys
Abstract
Background and purpose: Thyroid hormone receptor (TR) agonists are in clinical trials for the treatment of hypercholesterolaemia. As statins are the standard of clinical care, any new therapies must have adjunctive activity, when given in combination with statins. As already known for the statins, the cholesterol lowering effect of TR activation involves increased expression of the low-density lipoprotein receptor. Using animal models, we tested whether TR activation would have additive cholesterol lowering activity in the presence of effective doses of a statin.
Experimental approach: We evaluated the activity of a liver-targeted prodrug, MB07811, of a novel TH receptor beta agonist, MB07344, as monotherapy and in combination with atorvastatin in rabbits, dogs and monkeys.
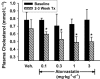
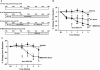
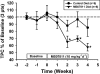
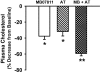
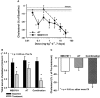
Key results: In rabbits, MB07344 (i.v.) decreased total plasma cholesterol (TPC) comparable to that achieved with a maximally effective dose of atorvastatin (p.o.). The addition of MB07344 to atorvastatin resulted in a further decrease in TPC. Similarly, the addition of MB07811 (p.o.) to atorvastatin treatment decreased TPC beyond the level achieved with either agent as monotherapy. In dogs and monkeys, atorvastatin and MB07811 were administered as monotherapy or in combination. Consistent with the rabbit studies, the combination treatment caused a greater decrease in TPC than either MB07811 or atorvastatin administered as monotherapy.
Conclusions and implications: We conclude that the effects of MB07811 and atorvastatin in lowering cholesterol are additive in animals. These results would encourage and support the demonstration of similarly improved efficacy of combination versus monotherapy with such agents in the clinic.
Figures
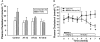
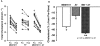
References
-
- Abrams JJ, Grundy SM. Cholesterol metabolism in hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism in man. J Lipid Res. 1981;22:323–338. - PubMed
-
- Aikawa M, Libby P. Lipid lowering reduces proteolytic and prothrombotic potential in rabbit atheroma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;902:140–152. - PubMed
-
- Alegret M, Verd JC, Diaz C, Hernandez G, Adzet T, Sanchez RM, et al. Effect of hypolipidemic drugs on key enzyme activities related to lipid metabolism in normolipidemic rabbits. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998;347:283–291. - PubMed
-
- Bakker O, Hudig F, Meijssen S, Wiersinga WM. Effects of triiodothyronine and amiodarone on the promoter of the human LDL receptor gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;249:517–521. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

