Chronic copper exposure exacerbates both amyloid and tau pathology and selectively dysregulates cdk5 in a mouse model of AD
- PMID: 19183260
- PMCID: PMC4096128
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.05901.x
Chronic copper exposure exacerbates both amyloid and tau pathology and selectively dysregulates cdk5 in a mouse model of AD
Abstract
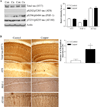
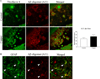
Excess copper exposure is thought to be linked to the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD) neuropathology. However, the mechanism by which copper affects the CNS remains unclear. To investigate the effect of chronic copper exposure on both beta-amyloid and tau pathologies, we treated young triple transgenic (3xTg-AD) mice with 250 ppm copper-containing water for a period of 3 or 9 months. Copper exposure resulted in altered amyloid precursor protein processing; increased accumulation of the amyloid precursor protein and its proteolytic product, C99 fragment, along with increased generation of amyloid-beta peptides and oligomers. These changes were found to be mediated via up-regulation of BACE1 as significant increases in BACE1 levels and deposits were detected around plaques in mice following copper exposure. Furthermore, tau pathology within hippocampal neurons was exacerbated in copper-exposed 3xTg-AD group. Increased tau phosphorylation was closely correlated with aberrant cdk5/p25 activation, suggesting a role for this kinase in the development of copper-induced tau pathology. Taken together, our data suggest that chronic copper exposure accelerates not only amyloid pathology but also tau pathology in a mouse model of AD.
Figures

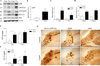



References
-
- Angeletti B, Waldron KJ, Freeman KB, Bawagan H, Hussain I, Miller CC, Lau KF, Tennant ME, Dennison C, Robinson NJ, Dingwall C. BACE1 cytoplasmic domain interacts with the copper chaperone for superoxide dismutase-1 and binds copper. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:17930–17937. - PubMed
-
- Armendariz AD, Gonzalez M, Loguinov AV, Vulpe CD. Gene expression profiling in chronic copper overload reveals upregulation of Prnp and App. Physiol Genomics. 2004;20:45–54. - PubMed
-
- Atwood CS, Scarpa RC, Huang X, Moir RD, Jones WD, Fairlie DP, Tanzi RE, Bush AI. Characterization of copper interactions with alzheimer amyloid beta peptides: identification of an attomolar-affinity copper binding site on amyloid beta1-42. J Neurochem. 2000;75:1219–1233. - PubMed
-
- Atwood CS, Moir RD, Huang X, Scarpa RC, Bacarra NM, Romano DM, Hartshorn MA, Tanzi RE, Bush AI. Dramatic aggregation of Alzheimer abeta by Cu(II) is induced by conditions representing physiological acidosis. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:12817–12826. - PubMed
-
- Augustinack JC, Sanders JL, Tsai LH, Hyman BT. Colocalization and fluorescence resonance energy transfer between cdk5 and AT8 suggests a close association in pre-neurofibrillary tangles and neurofibrillary tangles. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2002;61:557–564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

