Mycoplasma pneumoniae J-domain protein required for terminal organelle function
- PMID: 19183275
- PMCID: PMC5833977
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06602.x
Mycoplasma pneumoniae J-domain protein required for terminal organelle function
Abstract
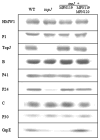
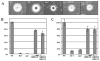
The cell wall-less prokaryote Mycoplasma pneumoniae causes tracheobronchitis and primary atypical pneumonia in humans. Colonization of the respiratory epithelium requires proper assembly of a complex, multifunctional, polar terminal organelle. Loss of a predicted J-domain protein also having domains unique to mycoplasma terminal organelle proteins (TopJ) resulted in a non-motile, adherence-deficient phenotype. J-domain proteins typically stimulate ATPase activity of Hsp70 chaperones to bind nascent peptides for proper folding, translocation or macromolecular assembly, or to resolve stress-induced protein aggregates. By Western immunoblotting all defined terminal organelle proteins examined except protein P24 remained at wild-type levels in the topJ mutant; previous studies established that P24 is required for normal initiation of terminal organelle formation. Nevertheless, terminal organelle proteins P1, P30, HMW1 and P41 failed to localize to a cell pole, and when evaluated quantitatively, P30 and HMW1 foci were undetectable in >40% of cells. Complementation of the topJ mutant with the recombinant wild-type topJ allele largely restored terminal organelle development, gliding motility and cytadherence. We propose that this J-domain protein, which localizes to the base of the terminal organelle in wild-type M. pneumoniae, functions in the late stages of assembly, positioning, or both, of nascent terminal organelles.
Figures




References
-
- Balish MF, Krause DC. Cytadherence and the cytoskeleton. In: Herrmann SRaR., editor. Molecular Biology and Pathogenicity of the Mycoplasmas. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers; 2002. pp. 491–518.
-
- Balish MF, Santurri RT, Ricci AM, Lee KK, Krause DC. Localization of Mycoplasma pneumoniae cytadherence-associated protein HMW2 by fusion with green fluorescent protein: implications for attachment organelle structure. Mol Microbiol. 2003;47:49–60. - PubMed
-
- Baseman JB, Morrison-Plummer J, Drouillard D, Puleo-Scheppke B, Tryon VV, Holt SC. Identification of a 32-kilodalton protein of Mycoplasma pneumoniae associated with hemadsorption. Isr J Med Sci. 1987;23:474–479. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

