The importance of endothelin-1 for microvascular dysfunction in diabetes
- PMID: 19183753
- PMCID: PMC2605330
- DOI: 10.2147/vhrm.s3920
The importance of endothelin-1 for microvascular dysfunction in diabetes
Abstract
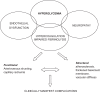
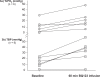
Most of the late diabetic complications such as retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy, have their basis in disturbed microvascular function. Structural and functional changes in the micro-circulation are present in diabetes mellitus irrespective of the organ studied, and the pathogenesis is complex. Endothelial dysfunction, characterized by an imbalance between endothelium-derived vasodilator and vasoconstrictor substances, plays an important role in the pathogenesis of diabetic microangiopathy. Increased circulating levels of endothelin-1 (ET-1), a potent vasoconstrictor peptide, has been found in patients with diabetes, and a positive correlation between plasma ET-1 levels and microangiopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes has been demonstrated. In addition to its direct vasoconstrictor effects, enhanced levels of ET-1 may contribute to endothelial dysfunction through inhibitory effects on nitric oxide (NO) production. Vascular endothelial dysfunction may precede insulin resistance, although the feature of insulin resistance syndrome includes factors that have negative effects on endothelial function. Furthermore, ET-1 induces a reduction in insulin sensitivity and may take part in the development of the metabolic syndrome. In the following, the mechanisms by which ET-1 contributes to the development of diabetic microangiopathy and the potentially beneficial effect of selective ET(A) receptor antagonists are discussed.
Keywords: ETA-receptor antagonist; diabetes mellitus; diabetic microangiopathy; endothelin-1; microcirculation.
Figures
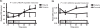
References
-
- Abassi ZA, Tate JE, Golomb E, et al. Role of neutral endopeptidase in the metabolism of endothelin. Hypertension. 1992;20:89–95. - PubMed
-
- Ahlborg G, Lindström J. Insulin sensitivity and big ET-1 conversion to ET-1 after ETA- or ETB-receptor blockade in humans. J Appl Physiol. 2002;93:2112–21. - PubMed
-
- Ak G, Buyukberber S, Sevinc A, et al. The relation between plasma endothelin-1 levels and metabolic control, risk factors, treatment modalities, and diabetic microangiopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complications. 2001;15:150–7. - PubMed
-
- Anfossi G, Russo I, Doronzo G, et al. Relevance of the vascular effects of insulin in the rationale of its therapeutical use. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2007;7:228–49. - PubMed
-
- Anggard E, Galton S, Rae G, et al. The fate of radioiodinated endothelin-1 and endothelin-3 in the rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1989;13:S46–S49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

