Brain ischemia and ischemic blood-brain barrier as etiological factors in sporadic Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 19183778
- PMCID: PMC2626921
- DOI: 10.2147/ndt.s3739
Brain ischemia and ischemic blood-brain barrier as etiological factors in sporadic Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
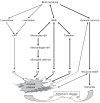
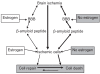
The development of neuronal death and amyloid plaques is a characteristic feature of ischemic- and Alzheimer-type dementia. An important aspect of neuronal loss and amyloid plaques are their topography and neuropathogenesis. This review was performed to present the hypothesis that different fragments of blood-borne amyloid precursor protein are able to enter the ischemic blood-brain barrier. Chronic disruption of the blood-brain barrier after ischemic injury was shown. As an effect of chronic ischemic blood-brain barrier injury, a visible connection of amyloid plaques with neurovasculature was observed. This neuropathology appears to have similar distribution and mechanisms to Alzheimer's disease. The usefulness of rival ischemic theory in elucidating the neuropathogenesis of amyloid plaques formation and neuronal death in Alzheimer's disorder is discussed.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid plaques; brain ischemia; dementia; ischemic blood-brain barrier; leukocytes; neuronal death; platelets.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sporadic Alzheimer's disease begins as episodes of brain ischemia and ischemically dysregulated Alzheimer's disease genes.Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Dec;48(3):500-15. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8439-1. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23519520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of ischemic blood-brain barrier on amyloid plaques development in Alzheimer's disease brain.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2007 May;4(2):121-9. doi: 10.2174/156720207780637207. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2007. PMID: 17504210 Review.
-
Post-Ischemic Permeability of the Blood-Brain Barrier to Amyloid and Platelets as a Factor in the Maturation of Alzheimer's Disease-Type Brain Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 27;24(13):10739. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310739. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathological opening of the blood-brain barrier to horseradish peroxidase and amyloid precursor protein following ischemia-reperfusion brain injury.Chemotherapy. 2005 Jul;51(4):223-6. doi: 10.1159/000086924. Epub 2005 Jul 6. Chemotherapy. 2005. PMID: 16006769
-
Is the ischemic blood-brain barrier insufficiency responsible for full-blown Alzheimer's disease?Neurol Res. 2006 Sep;28(6):665-71. doi: 10.1179/016164106X130399. Neurol Res. 2006. PMID: 16945220 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between white matter lesions and cerebral Aβ burden.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 24;13(9):e0204313. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204313. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30248123 Free PMC article.
-
A Scoping Review of Alzheimers Disease Hypotheses: An Array of Uni- and Multi-Factorial Theories.J Alzheimers Dis. 2024;99(3):843-856. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230772. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 38788067 Free PMC article.
-
The Mitochondrial Enzyme 17βHSD10 Modulates Ischemic and Amyloid-β-Induced Stress in Primary Mouse Astrocytes.eNeuro. 2022 Oct 6;9(5):ENEURO.0040-22.2022. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0040-22.2022. Print 2022 Sep-Oct. eNeuro. 2022. PMID: 36096650 Free PMC article.
-
Tau Protein Dysfunction after Brain Ischemia.J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;66(2):429-437. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180772. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 30282370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sporadic Alzheimer's disease begins as episodes of brain ischemia and ischemically dysregulated Alzheimer's disease genes.Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Dec;48(3):500-15. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8439-1. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23519520 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alzheimer A. Über eine eigenartige Erkrankung der Hirnrinde. Allg Z Psychiatr Psych Gericht Med (Berlin) 1907;64:146–8.
-
- Anfuso CD, Assero G, Lupo G, et al. Amyloid beta (1–42) and its beta (25–35) fragment induce activation and membrane translocation of cytosolic phospholipase A (2) in bovine retina capillary pericytes. Biochem Biophys Acta. 2004;1686:125–38. - PubMed
-
- Arshavsky YL. Alzheimer’s disease, brain immune privilege and memory: A hypothesis. J Neural Transm. 2006;113:1697–707. - PubMed
-
- Attems J, Jellinger KA. Only cerebral capillary amyloid angiopathy correlates with Alzheimer pathology – a pilot study. Acta Neuropathol. 2004;107:83–90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

