Inflammation as a potential mediator for the association between periodontal disease and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 19183779
- PMCID: PMC2626915
- DOI: 10.2147/ndt.s3610
Inflammation as a potential mediator for the association between periodontal disease and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
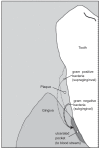
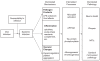
Periodontal disease (PDD) is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, and mortality in many studies, while other studies have begun to suggest an association of PDD with Alzheimer's disease (AD). This paper discusses how infectious pathogens and systemic infection may play a role in AD. The roles of infection and inflammation are addressed specifically with regard to known AD pathologic lesions including senile plaques, neuron death, neurofibrillary tangles, and cerebrovascular changes. A testable model of proposed pathways between periodontal infection and AD is presented including three possible mechanisms: a) direct effects of infectious pathogens, b) inflammatory response to pathogens, and c) the effects on vascular integrity. The role of gene polymorphisms is discussed, including apolipoprotein (APOE) varepsilon4 as a pro-inflammatory and pro-infection genotype.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; infection; inflammation; periodontal disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinicopathologic studies in cognitively healthy aging and Alzheimer's disease: relation of histologic markers to dementia severity, age, sex, and apolipoprotein E genotype.Arch Neurol. 1998 Mar;55(3):326-35. doi: 10.1001/archneur.55.3.326. Arch Neurol. 1998. PMID: 9520006
-
The apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 does not correlate with the number of senile plaques or neurofibrillary tangles in patients with Alzheimer's disease.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1996 Oct;61(4):352-6. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.61.4.352. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1996. PMID: 8890772 Free PMC article.
-
[Expression of apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer's disease and its significance].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2005 Sep;34(9):556-60. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 16468304 Chinese.
-
Perspectives on the Role of APOE4 as a Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2021 Dec 27;5(1):899-910. doi: 10.3233/ADR-210027. eCollection 2021. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2021. PMID: 35088039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Independent and Correlated Role of Apolipoprotein E ɛ4 Genotype and Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 in Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;77(1):15-31. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200607. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020. PMID: 32804091 Review.
Cited by
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced periodontitis could contribute to cognitive impairment in Sprague-Dawley rats via the P38 MAPK signaling pathway.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Mar 28;17:1141339. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1141339. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37056710 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Tooth Loss and the Apolipoprotein E ɛ4 Allele on Mild Memory Impairment in the Fujiwara-kyo Study of Japan: A Nested Case-Control Study.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;55(2):575-583. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160638. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 27716671 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease and symbiotic microbiota: an evolutionary medicine perspective.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019 Aug;1449(1):3-24. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14129. Epub 2019 Jun 10. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019. PMID: 31180143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the role of Porphyromonas gingivalis in periodontitis to determine a causative relationship with Alzheimer's disease.J Oral Microbiol. 2019 Jan 29;11(1):1563405. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2018.1563405. eCollection 2019. J Oral Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30728914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salivary biomarkers: The early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease.Aging Med (Milton). 2024 Feb 20;7(2):202-213. doi: 10.1002/agm2.12282. eCollection 2024 Apr. Aging Med (Milton). 2024. PMID: 38725701 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aiello AE, Haan MN, Blythe L, et al. The influence of latent viral infection on rate of cognitive decline over 4 years. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54:1046–54. - PubMed
-
- Airila-Mansson S, Soder B, Kari K, et al. Influence of combinations of bacteria on the levels of prostaglandin E2, interleukin-1β, and granulocyte elastase in gingival crevicular fluid and on the severity of periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 2006;77:1025–31. - PubMed
-
- Arbes SJ, Slade GD, Beck JD. Association between extent of periodontal attachment loss and self-reported history of heart-attack: An analysis of NHANES III data. J Dent Res. 1999;78:1777–82. - PubMed
-
- Balin BJ, Appelt DM. Role of infection in Alzheimer’s disease. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2001;101:S1–6. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

