Optimizing electroporation conditions in primary and other difficult-to-transfect cells
- PMID: 19183796
- PMCID: PMC2628074
Optimizing electroporation conditions in primary and other difficult-to-transfect cells
Abstract
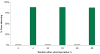
Electroporation is a valuable tool for nucleic acid delivery because it can be used for a wide variety of cell types. Many scientists are shifting toward the use of cell types that are more relevant to in vivo applications, including primary cells, which are considered difficult to transfect. The ability to electroporate these cell types with nucleic acid molecules of interest at a relatively high efficiency while maintaining cell viability is essential for elucidating the pathway(s) in which a gene product is involved. We present data demonstrating that by optimizing electroporation parameters, nucleic acid molecules can be delivered in a highly efficient manner. We display transfection results for primary and difficult-to-transfect cell types including human primary fibroblasts, human umbilical vein endothelial cells, Jurkat cells, and two neuroblastoma cell lines [SK-N-SH (human) and Neuro-2A (mouse)] with plasmid DNAs and siRNAs. Our data demonstrate that by determining proper electroporation conditions, glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA was silenced in Jurkat cells when compared with negative control siRNA electroporations as early as 4 h post-transfection. Other experiments demonstrated that optimized electroporation conditions using a fluorescently labeled transfection control siRNA resulted in 75% transfection efficiency for Neuro-2A, 93% for human primary fibroblasts, and 94% for HUVEC cells, as analyzed by flow cytometry.
Keywords: HUVEC; Jurkat; MXcell; Neuro-2a; SK-N-SH; electroporation; human primary fibroblasts; mammalian cells; neuroblastoma; primary cells transfection.
Figures
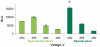

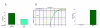
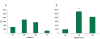
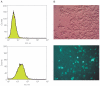
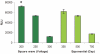
Similar articles
-
Using the gene pulser MXcell electroporation system to transfect primary cells with high efficiency.J Vis Exp. 2010 Jan 7;(35):1662. doi: 10.3791/1662. J Vis Exp. 2010. PMID: 20057352 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmid DNA and siRNA transfection of intestinal epithelial monolayers by electroporation.Int J Pharm. 2006 Jun 6;315(1-2):122-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.02.022. Epub 2006 Mar 6. Int J Pharm. 2006. PMID: 16564652
-
The preparation of primary hematopoietic cell cultures from murine bone marrow for electroporation.J Vis Exp. 2009 Jan 6;(23):1026. doi: 10.3791/1026. J Vis Exp. 2009. PMID: 19229174 Free PMC article.
-
Electroporation Knows No Boundaries: The Use of Electrostimulation for siRNA Delivery in Cells and Tissues.J Biomol Screen. 2015 Sep;20(8):932-42. doi: 10.1177/1087057115579638. Epub 2015 Apr 7. J Biomol Screen. 2015. PMID: 25851034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single cell optical transfection.J R Soc Interface. 2010 Jun 6;7(47):863-71. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2009.0463. Epub 2010 Jan 11. J R Soc Interface. 2010. PMID: 20064901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electric organ discharge from electric eel facilitates DNA transformation into teleost larvae in laboratory conditions.PeerJ. 2023 Dec 4;11:e16596. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16596. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 38077423 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic Mechanoporation: Current Progress and Applications in Stem Cells.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 May 17;14(5):256. doi: 10.3390/bios14050256. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38785730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AQP5-1364A/C polymorphism and the AQP5 expression influence sepsis survival and immune cell migration: a prospective laboratory and patient study.J Transl Med. 2016 Nov 21;14(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-1079-2. J Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27871297 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of bionic array electric field focusing in plasmid DNA-based gene electrotransfer.Gene Ther. 2016 Apr;23(4):369-79. doi: 10.1038/gt.2016.8. Epub 2016 Jan 30. Gene Ther. 2016. PMID: 26826485 Free PMC article.
-
Protein function analysis: rapid, cell-based siRNA-mediated ablation of endogenous expression with simultaneous ectopic replacement.Cytotechnology. 2010 Apr;62(2):495-503. doi: 10.1007/s10616-010-9270-4. Cytotechnology. 2010. PMID: 20390449 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shigekawa K, Dower WJ. Electroporation of eukaryotes and prokaryotes: A general approach to the introduction of macromolecules into cells. Biotechniques. 1988;6:742–751. - PubMed
-
- Rols M-P, Golzio M, Delteil C, Teissie J. In vitro delivery of drugs and other molecules to cells. In: Jaroszeski MJ, Heller R, Gilbert R, editors. Methods in Molecular Medicine. Vol. 37. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2000. pp. 83–97. - PubMed
-
- Rols MP. Electropermeabilization: A physical method for the delivery of therapeutic molecules into cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1758:423–428. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
