Optimizing electroporation conditions in primary and other difficult-to-transfect cells
- PMID: 19183796
- PMCID: PMC2628074
Optimizing electroporation conditions in primary and other difficult-to-transfect cells
Abstract
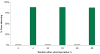
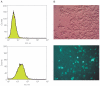
Electroporation is a valuable tool for nucleic acid delivery because it can be used for a wide variety of cell types. Many scientists are shifting toward the use of cell types that are more relevant to in vivo applications, including primary cells, which are considered difficult to transfect. The ability to electroporate these cell types with nucleic acid molecules of interest at a relatively high efficiency while maintaining cell viability is essential for elucidating the pathway(s) in which a gene product is involved. We present data demonstrating that by optimizing electroporation parameters, nucleic acid molecules can be delivered in a highly efficient manner. We display transfection results for primary and difficult-to-transfect cell types including human primary fibroblasts, human umbilical vein endothelial cells, Jurkat cells, and two neuroblastoma cell lines [SK-N-SH (human) and Neuro-2A (mouse)] with plasmid DNAs and siRNAs. Our data demonstrate that by determining proper electroporation conditions, glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA was silenced in Jurkat cells when compared with negative control siRNA electroporations as early as 4 h post-transfection. Other experiments demonstrated that optimized electroporation conditions using a fluorescently labeled transfection control siRNA resulted in 75% transfection efficiency for Neuro-2A, 93% for human primary fibroblasts, and 94% for HUVEC cells, as analyzed by flow cytometry.
Keywords: HUVEC; Jurkat; MXcell; Neuro-2a; SK-N-SH; electroporation; human primary fibroblasts; mammalian cells; neuroblastoma; primary cells transfection.
Figures
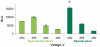

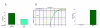
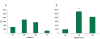
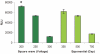
References
-
- Shigekawa K, Dower WJ. Electroporation of eukaryotes and prokaryotes: A general approach to the introduction of macromolecules into cells. Biotechniques. 1988;6:742–751. - PubMed
-
- Rols M-P, Golzio M, Delteil C, Teissie J. In vitro delivery of drugs and other molecules to cells. In: Jaroszeski MJ, Heller R, Gilbert R, editors. Methods in Molecular Medicine. Vol. 37. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2000. pp. 83–97. - PubMed
-
- Rols MP. Electropermeabilization: A physical method for the delivery of therapeutic molecules into cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1758:423–428. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
