Procedural pain heart rate responses in massaged preterm infants
- PMID: 19185352
- PMCID: PMC2694508
- DOI: 10.1016/j.infbeh.2008.12.001
Procedural pain heart rate responses in massaged preterm infants
Abstract
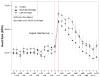
Heart rate (HR) responses to the removal of a monitoring lead were assessed in 56 preterm infants who received moderate pressure, light pressure or no massage therapy. The infants who received moderate pressure massage therapy exhibited lower increases in HR suggesting an attenuated pain response. The heart rate of infants who received moderate pressure massage also returned to baseline faster than the heart rate of the other two groups, suggesting a faster recovery rate.
Figures
References
-
- Anand KJS. International Evidence-Based Group for Neonatal Pain. Consensus statement for the prevention and management of pain in the newborn. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2001;155:173–180. - PubMed
-
- Gray L, Watt L, Blass EM. Skin-to-skin contact is analgesic in healthy newborns. Pediatrics. 2000;105:e14. - PubMed
-
- Grunau R. Long-term consequences of pain in human neonates. In: Anand KJ, Stevens B, McGrath PJ, editors. Pain in Neonates. 2nd Revised and Enlarged. Vol. 10. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science; 2000. pp. 55–76.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical