Structural basis for recognition of diubiquitins by NEMO
- PMID: 19185524
- PMCID: PMC2749619
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.01.012
Structural basis for recognition of diubiquitins by NEMO
Abstract
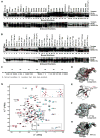
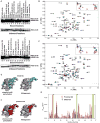
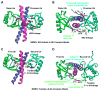
NEMO is the regulatory subunit of the IkappaB kinase (IKK) in NF-kappaB activation, and its CC2-LZ region interacts with Lys63 (K63)-linked polyubiquitin to recruit IKK to receptor signaling complexes. In vitro, CC2-LZ also interacts with tandem diubiquitin. Here we report the crystal structure of CC2-LZ with two dimeric coiled coils representing CC2 and LZ, respectively. Surprisingly, mutagenesis and nuclear magnetic resonance experiments reveal that the binding sites for diubiquitins at LZ are composites of both chains and that each ubiquitin in diubiquitins interacts with symmetrical NEMO asymmetrically. For tandem diubiquitin, the first ubiquitin uses the conserved hydrophobic patch and the C-terminal tail, while the second ubiquitin uses an adjacent surface patch. For K63-linked diubiquitin, the proximal ubiquitin uses its conserved hydrophobic patch, while the distal ubiquitin mostly employs the C-terminal arm including the K63 linkage residue. These studies uncover the energetics and geometry for mutual recognition of NEMO and diubiquitins.
Figures
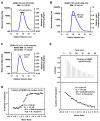
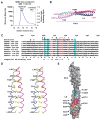
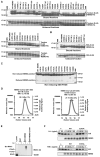
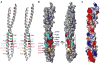
References
-
- Agou F, Ye F, Goffinont S, Courtois G, Yamaoka S, Israel A, Veron M. NEMO trimerizes through its coiled-coil C-terminal domain. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:17464–17475. - PubMed
-
- Cook WJ, Jeffrey LC, Kasperek E, Pickart CM. Structure of tetraubiquitin shows how multiubiquitin chains can be formed. J Mol Biol. 1994;236:601–609. - PubMed
-
- Courtois G, Gilmore TD. Mutations in the NF-kappaB signaling pathway: implications for human disease. Oncogene. 2006;25:6831–6843. - PubMed
-
- Dominguez C, Boelens R, Bonvin AM. HADDOCK: a protein-protein docking approach based on biochemical or biophysical information. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:1731–1737. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

