The brain hypocretins and their receptors: mediators of allostatic arousal
- PMID: 19185540
- PMCID: PMC3791851
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2008.12.018
The brain hypocretins and their receptors: mediators of allostatic arousal
Abstract
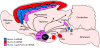
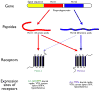
The hypocretins (abbreviated 'Hcrts' - also called 'orexins') are two neuropeptides secreted exclusively by a small population of neurons in the lateral hypothalamus. These peptides bind to two receptors located throughout the brain in nuclei associated with diverse cognitive and physiological functions. Initially, the brain Hcrt system was found to have a major role in the regulation of sleep/wake transitions. More recent studies indicate Hcrts may play a role in other physiological functions, including food intake, addiction, and stress. Taken together, these studies suggest a general role for Hcrts in mediating arousal, especially when an organism must respond to unexpected stressors and challenges in the environment.
Figures
References
-
- Lin L, Faraco J, Li R, Kadotani H, Rogers W, Lin X, Qiu X, de Jong PJ, Nishino S, Mignot E. The sleep disorder canine narcolepsy is caused by a mutation in the hypocretin (orexin) receptor 2 gene. Cell. 1999;98:365–376. - PubMed
-
- Chemelli RM, Willie JT, Sinton CM, Elmquist JK, Scammell T, Lee C, Richardson JA, Williams SC, Xiong Y, Kisanuki Y, et al. Narcolepsy in orexin knockout mice: molecular genetics of sleep regulation. Cell. 1999;98:437–451. These studies were the first to indicate that dyregulation of the Hcrt system is sufficient to cause narcolepsy. These seminal publications greatly increased our understanding of the cause of narcolepsy and sleep disorders and also discovered a crucial role for the Hcrts in the maintenance of wakefulness and arousal. - PubMed
-
- Hara J, Beuckmann CT, Nambu T, Willie JT, Chemelli RM, Sinton CM, Sugiyama F, Yagami K, Goto K, Yanagisawa M, et al. Genetic ablation of orexin neurons in mice results in narcolepsy, hypophagia, and obesity. Neuron. 2001;30:345–354. - PubMed
-
- Nishino S, Ripley B, Overeem S, Lammers GJ, Mignot E. Hypocretin (orexin) deficiency in human narcolepsy. Lancet. 2000;355:39–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

