IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated cancer
- PMID: 19185845
- PMCID: PMC2667107
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.01.001
IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated cancer
Erratum in
- Cancer Cell. 2009 Mar 3;15(3):241
Abstract
Colitis-associated cancer (CAC) is the most serious complication of inflammatory bowel disease. Proinflammatory cytokines have been suggested to regulate preneoplastic growth during CAC tumorigenesis. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is a multifunctional NF-kappaB-regulated cytokine that acts on epithelial and immune cells. Using genetic tools, we now demonstrate that IL-6 is a critical tumor promoter during early CAC tumorigenesis. In addition to enhancing proliferation of tumor-initiating cells, IL-6 produced by lamina propria myeloid cells protects normal and premalignant intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) from apoptosis. The proliferative and survival effects of IL-6 are largely mediated by the transcription factor Stat3, whose IEC-specific ablation has profound impact on CAC tumorigenesis. Thus, the NF-kappaB-IL-6-Stat3 cascade is an important regulator of the proliferation and survival of tumor-initiating IECs.
Conflict of interest statement
All other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
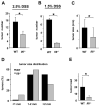
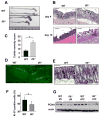
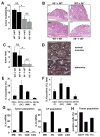
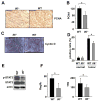
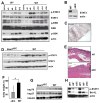
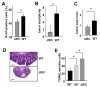
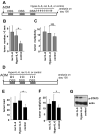
Comment in
-
Inflammation and cancer: IL-6 and STAT3 complete the link.Cancer Cell. 2009 Feb 3;15(2):79-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.01.009. Cancer Cell. 2009. PMID: 19185839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atreya R, Mudter J, Finotto S, Mullberg J, Jostock T, Wirtz S, Schutz M, Bartsch B, Holtmann M, Becker C, et al. Blockade of interleukin 6 trans signaling suppresses T-cell resistance against apoptosis in chronic intestinal inflammation: evidence in crohn disease and experimental colitis in vivo. Nat Med. 2000;6:583–588. - PubMed
-
- Atreya R, Neurath MF. Involvement of IL-6 in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease and colon cancer. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2005;28:187–196. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F, Charles KA, Mantovani A. Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and promotion of malignant disease. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:211–217. - PubMed
-
- Becker C, Fantini MC, Schramm C, Lehr HA, Wirtz S, Nikolaev A, Burg J, Strand S, Kiesslich R, Huber S, et al. TGF-beta suppresses tumor progression in colon cancer by inhibition of IL-6 trans-signaling. Immunity. 2004;21:491–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

