Calcium-activated potassium channels and endothelial dysfunction: therapeutic options?
- PMID: 19187341
- PMCID: PMC2697708
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00052.x
Calcium-activated potassium channels and endothelial dysfunction: therapeutic options?
Abstract
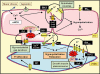
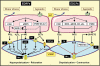
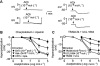
The three subtypes of calcium-activated potassium channels (K(Ca)) of large, intermediate and small conductance (BK(Ca), IK(Ca) and SK(Ca)) are present in the vascular wall. In healthy arteries, BK(Ca) channels are preferentially expressed in vascular smooth muscle cells, while IK(Ca) and SK(Ca) are preferentially located in endothelial cells. The activation of endothelial IK(Ca) and SK(Ca) contributes to nitric oxide (NO) generation and is required to elicit endothelium-dependent hyperpolarizations. In the latter responses, the hyperpolarization of the smooth muscle cells is evoked either via electrical coupling through myo-endothelial gap junctions or by potassium ions, which by accumulating in the intercellular space activate the inwardly rectifying potassium channel Kir2.1 and/or the Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase. Additionally, endothelium-derived factors such as cytochrome P450-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids and under some circumstances NO, prostacyclin, lipoxygenase products and hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) hyperpolarize and relax the underlying smooth muscle cells by activating BK(Ca). In contrast, cytochrome P450-derived 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid and various endothelium-derived contracting factors inhibit BK(Ca). Aging and cardiovascular diseases are associated with endothelial dysfunctions that can involve a decrease in NO bioavailability, alterations of EDHF-mediated responses and/or enhanced production of endothelium-derived contracting factors. Because potassium channels are involved in these endothelium-dependent responses, activation of endothelial and/or smooth muscle K(Ca) could prevent the occurrence of endothelial dysfunction. Therefore, direct activators of these potassium channels or compounds that regulate their activity or their expression may be of some therapeutic interest. Conversely, blockers of IK(Ca) may prevent restenosis and that of BK(Ca) channels sepsis-dependent hypotension.
Figures




References
-
- Abdelrrahmane A, Salvail D, Dumoulin M, Garon J, Cadieux A, Rousseau E. Direct activation of KCa channel in airway smooth muscle by nitric oxide: involvement of a nitrothiosylation mechanism? Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998;19:485–497. - PubMed
-
- Alonso-Galicia M, Drummond HA, Reddy KK, Falck JR, Roman RJ. Inhibition of 20-HETE production contributes to the vascular responses to nitric oxide. Hypertension. 1997;29:320–325. - PubMed
-
- Amberg GC, Santana LF. Downregulation of the BK channel beta1 subunit in genetic hypertension. Circ Res. 2003;93:965–971. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

