A noncoding RNA gene on chromosome 10p15.3 may function upstream of hTERT
- PMID: 19187532
- PMCID: PMC2661890
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-10-5
A noncoding RNA gene on chromosome 10p15.3 may function upstream of hTERT
Abstract
Background: We attempted to clone candidate genes on 10p 14-15 which may regulate hTERT expression, through exon trapping using 3 BAC clones covering the region. After obtaining 20 exons, we examined the function of RGM249 (RGM: RNA gene for miRNAs) we cloned from primary cultured human hepatocytes and hepatoma cell lines. We confirmed approximately 20 bp products digested by Dicer, and investigated the function of this cloned gene and its involvement in hTERT expression by transfecting the hepatoma cell lines with full-length dsRNA, gene-specific designed siRNA, and shRNA-generating plasmid.
Results: RGM249 showed cancer-dominant intense expression similar to hTERT in cancer cell lines, whereas very weak expression was evident in human primary hepatocytes without telomerase activity. This gene was predicted to be a noncoding precursor RNA gene. Interestingly, RGM249 dsRNA, siRNA, and shRNA inhibited more than 80% of hTERT mRNA expression. In contrast, primary cultured cells overexpressing the gene showed no significant change in hTERT mRNA expression; the overexpression of the gene strongly suppressed hTERT mRNA in poorly differentiated cells.
Conclusion: These findings indicate that RGM249 might be a microRNA precursor gene involved in the differentiation and function upstream of hTERT.
Figures
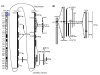



 RGM249 mRNA, ▯ hTERT mRNA,
RGM249 mRNA, ▯ hTERT mRNA,  RPL22 mRNA. d) Quantitative evaluation of the inhibitory effect of RGM249 shRNA on RGM249 mRNA, hTERT mRNA, and RPL22 mRNA. From left, transfection using only transfection reagents, LacZ shRNA as the gene control, wtRGM249 shRNA, and mt-1RGM249 or mt-2RGM249 shRNA with a different mutation (a nucleotide T or C) in the functional sequence. A total of 5 transfections were performed and data were statistically analyzed using the Mann-Whitney test. Compared with LacZ shRNA, RGM249 and mt-1RGM249 shRNA significantly suppressed hTERT mRNA (P = 0.002 and P = 0.034, respectively). mt-1RGM249 and mt-2RGM249 correspond to those in Table 2. ▯ RGM249 mRNA,
RPL22 mRNA. d) Quantitative evaluation of the inhibitory effect of RGM249 shRNA on RGM249 mRNA, hTERT mRNA, and RPL22 mRNA. From left, transfection using only transfection reagents, LacZ shRNA as the gene control, wtRGM249 shRNA, and mt-1RGM249 or mt-2RGM249 shRNA with a different mutation (a nucleotide T or C) in the functional sequence. A total of 5 transfections were performed and data were statistically analyzed using the Mann-Whitney test. Compared with LacZ shRNA, RGM249 and mt-1RGM249 shRNA significantly suppressed hTERT mRNA (P = 0.002 and P = 0.034, respectively). mt-1RGM249 and mt-2RGM249 correspond to those in Table 2. ▯ RGM249 mRNA,  hTERT mRNA,
hTERT mRNA,  RPL22 mRNA, *: P < 0.05; **: P < 0.01. Quantitative evaluation of the suppressive effect of shRNA in which the measurement, in the case without siRNA, was regarded as 100% for standardization (N = 5). (e) Telomerase activity was quantitatively compared using image analyzer between transfectants with LacZ shRNA (in proliferative state) and RGM249 shRNA (in senesced state) and RGM249 shRNA, and was compared with the parental cells (112 and 54, respectively, which had an intensity of 100). Although the results depended on the timing of cell harvests after transfection, telomerase activity in transfectants with RGM249 shRNA was reduced to approximately half compared with that in parental cells, and we observed a periodicity of 6 bp due to reduced telomerase in the shRNA lane. NC: telomerase negative control.
RPL22 mRNA, *: P < 0.05; **: P < 0.01. Quantitative evaluation of the suppressive effect of shRNA in which the measurement, in the case without siRNA, was regarded as 100% for standardization (N = 5). (e) Telomerase activity was quantitatively compared using image analyzer between transfectants with LacZ shRNA (in proliferative state) and RGM249 shRNA (in senesced state) and RGM249 shRNA, and was compared with the parental cells (112 and 54, respectively, which had an intensity of 100). Although the results depended on the timing of cell harvests after transfection, telomerase activity in transfectants with RGM249 shRNA was reduced to approximately half compared with that in parental cells, and we observed a periodicity of 6 bp due to reduced telomerase in the shRNA lane. NC: telomerase negative control.


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

