Radiation produces differential changes in cytokine profiles in radiation lung fibrosis sensitive and resistant mice
- PMID: 19187543
- PMCID: PMC2663566
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-8722-2-6
Radiation produces differential changes in cytokine profiles in radiation lung fibrosis sensitive and resistant mice
Abstract
Background: Recent research has supported that a variety of cytokines play important roles during radiation-induced lung toxicity. The present study is designed to investigate the differences in early cytokine induction after radiation in sensitive (C57BL/6) and resistant mice (C3H).
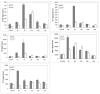
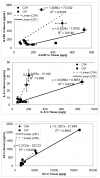
Results: Twenty-two cytokines in the lung tissue homogenates, bronchial lavage (BAL) fluids, and serum from 3, 6, 12, 24 hrs to 1 week after 12 Gy whole lung irradiation were profiled using a microsphere-based multiplexed cytokine assay. The majority of cytokines had similar baseline levels in C57BL/6 and C3H mice, but differed significantly after radiation. Many, including granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and keratinocyte-derived chemokine (KC) were elevated significantly in specimens from both strains. They usually peaked at about 3-6 hrs in C57BL/6 and 6-12 hrs in C3H. At 6 hrs in lung tissue, G-CSF, IL-6, and KC increased 6, 8, and 11 fold in C57BL/6 mice, 4, 3, and 3 fold in the C3H mice, respectively. IL-6 was 10-fold higher at 6 hrs in the C57BL/6 BAL fluid than the C3H BAL fluid. MCP-1, IP-10, and IL-1alpha also showed some differences between strains in the lung tissue and/or serum. For the same cytokine and within the same strain of mice, there were significant linear correlations between lung tissue and BAL fluid levels (R2 ranged 0.46-0.99) and between serum and tissue (R2 ranged 0.56-0.98).
Conclusion: Radiation induced earlier and greater temporal changes in multiple cytokines in the pulmonary fibrosis sensitive mice. Positive correlation between serum and tissue levels suggests that blood may be used as a surrogate marker for tissue.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Compartmental responses after thoracic irradiation of mice: strain differences.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005 Jul 1;62(3):862-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.02.037. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. PMID: 15936571
-
Acute adaptive immune response correlates with late radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice.Radiat Oncol. 2015 Feb 20;10:45. doi: 10.1186/s13014-015-0359-y. Radiat Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25889053 Free PMC article.
-
An experimental model-based exploration of cytokines in ablative radiation-induced lung injury in vivo and in vitro.Lung. 2015 Jun;193(3):409-19. doi: 10.1007/s00408-015-9705-y. Epub 2015 Mar 7. Lung. 2015. PMID: 25749666
-
Identification of miRNA signatures associated with radiation-induced late lung injury in mice.PLoS One. 2020 May 11;15(5):e0232411. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232411. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32392259 Free PMC article.
-
A survey of changing trends in modelling radiation lung injury in mice: bringing out the good, the bad, and the uncertain.Lab Invest. 2016 Sep;96(9):936-49. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2016.76. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Lab Invest. 2016. PMID: 27479087 Review.
Cited by
-
Defensin DEFB103 bidirectionally regulates chemokine and cytokine responses to a pro-inflammatory stimulus.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1232. doi: 10.1038/srep01232. Epub 2013 Feb 6. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23390582 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Blood Biomarkers of Angiogenesis and Immune Modulation after Radiation Therapy and Their Association with Outcomes in Thoracic Malignancies.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 16;13(22):5725. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225725. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830880 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation-induced fibrosis: mechanisms and implications for therapy.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015 Nov;141(11):1985-94. doi: 10.1007/s00432-015-1974-6. Epub 2015 Apr 25. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25910988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the Combined Anticancer Response of Checkpoint Inhibitor Immunotherapy and FAP-Targeted Molecular Radiotherapy in Murine Models of Melanoma and Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 21;14(19):4575. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194575. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230500 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotective effect of zingerone against oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis induced by cisplatin or gamma radiation in rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018 Aug;391(8):819-832. doi: 10.1007/s00210-018-1506-4. Epub 2018 May 7. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29736620
References
-
- Emami B, Lyman J, Brown A, Coia L, Goitein M, Munzenrider JE, Shank B, Solin LJ, Wesson M. Tolerance of normal tissues to therapeutic irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1991;21:109–122. - PubMed
-
- Severin E, Greve B, Pascher E, Wedemeyer N, Hacker-Klom U, Silling G, Kienast J, Willich N, Gohde W. Evidence for predictive validity of blood assays to evaluate individual radiosensitivity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;64:242–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

