Significant vitamin D deficiency in youth with type 1 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 19187735
- PMCID: PMC2635941
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2008.07.015
Significant vitamin D deficiency in youth with type 1 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
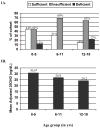
Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D was measured in 128 youth with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Less than 25% of the patients were vitamin D sufficient. Because individuals with type 1 diabetes mellitus possess multiple risk factors for skeletal fragility, ensuring vitamin D sufficiency throughout childhood and adolescence in this population seems especially warranted.
Figures
Comment in
-
Overall health in youth with type 1 diabetes.J Pediatr. 2009 Jan;154(1):A2. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2008.11.019. J Pediatr. 2009. PMID: 19187721 No abstract available.
-
They're still kids.J Pediatr. 2009 Jan;154(1):7-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2008.09.028. J Pediatr. 2009. PMID: 19187730 No abstract available.
References
-
- Holick MF. High prevalence of vitamin D inadequacy and implications for health. Mayo Clin Proc. 2006;81:353–73. - PubMed
-
- El Hajj FG, Nabulsi M, Choucair M, Salamoun M, Hajj SC, Kizirian A, et al. Hypovitaminosis D in healthy schoolchildren. Pediatrics. 2001;107:E53. - PubMed
-
- Tuominen JT, Impivaara O, Puukka P, Ronnemaa T. Bone mineral density in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1999;22:1196–200. - PubMed
-
- Miazgowski T, Czekalski S. A 2-year follow-up study on bone mineral density and markers of bone turnover in patients with long-standing insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Osteoporos Int. 1998;8:399–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

