An unexpected type of ribosomes induced by kasugamycin: a look into ancestral times of protein synthesis?
- PMID: 19187763
- PMCID: PMC2967816
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.12.014
An unexpected type of ribosomes induced by kasugamycin: a look into ancestral times of protein synthesis?
Abstract
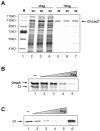
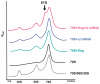
Translation of leaderless mRNAs, lacking ribosomal recruitment signals other than the 5'-terminal AUG-initiating codon, occurs in all three domains of life. Contemporary leaderless mRNAs may therefore be viewed as molecular fossils resembling ancestral mRNAs. Here, we analyzed the phenomenon of sustained translation of a leaderless mRNA in the presence of the antibiotic kasugamycin. Unexpected from the known in vitro effects of the drug, kasugamycin induced the formation of stable approximately 61S ribosomes in vivo, which were proficient in selectively translating leaderless mRNA. 61S particles are devoid of more than six proteins of the small subunit, including the functionally important proteins S1 and S12. The lack of these proteins could be reconciled with structural changes in the 16S rRNA. These studies provide in vivo evidence for the functionality of ribosomes devoid of multiple proteins and shed light on the evolutionary history of ribosomes.
Figures





Comment in
-
Less is more for leaderless mRNA translation.Mol Cell. 2009 Jan 30;33(2):141-2. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.01.006. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19187755
References
-
- Belanger F, Gagnon MG, Steinberg SV, Cunningham PR, Brakier-Gingras L. Study of the functional interaction of the 900 Tetraloop of 16S ribosomal RNA with helix 24 within the bacterial ribosome. J. Mol. Bio.l. 2004;338:683–693. - PubMed
-
- Blattner FR, Plunkett G, 3rd, Bloch CA, Perna NT, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Vides J, Glasner JD, Rode CK, Mayhew GF, et al. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science. 1997;277:1453–1474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

